32-inch monitor purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- The most important things in a nutshell
- 32-inch monitors make it easy to work with several programmes on the computer simultaneously. They are also suitable for watching TV, streaming and playing games.
- In addition to the viewing-angle-stable IPS panels, there are also the high-contrast VA panels and the responsive TN panels.
- Special technologies from AMD and Nvidia ensure a smooth picture.
- When buying, it is not only the display technology that matters, but also the resolution, refresh rate, pixel density, response time and connections.
- Correct positioning is important to prevent posture problems.
32-inch monitor – the optimal size?
Computer monitors come in a wide variety of sizes, from 21.5 inches upwards. In practice, however, small monitors are often problematic because too little can be seen on them. The rule “the bigger, the better” should also be taken with a grain of salt, as there is usually only limited space available on the desk. In addition, a larger monitor requires a greater sitting distance. Monitors with a screen diagonal of 32 inches are considered a good solution because their size makes it easier to work with PC applications and most desks are large enough for them.
32-inch monitors are available in different formats that represent the ratio of width to height. The 21:9 format, for example, is excellent for those who like to watch films via the PC. Office applications that require a lot of space to display also benefit from the widescreen format. Likewise, a large screen is advantageous for gamers, who can immerse themselves more in the gaming action.
The different panel types
From a functional point of view, the panel is the most important component of a monitor. The liquid crystals used in LCD technology can be controlled in different ways. In the meantime, three processes have become established.
IPS panel
The abbreviation stands for “In Plane Switching”. The image of these panels is very sharp in contrast. The arrangement of the molecules is not perpendicular but parallel to the display surface. This results in much better readability from a lateral viewing angle. In addition, the pixels react faster, so there are no lagging effects in fast videos or games. Therefore, this type of panel is well suited for applications such as image editing and video editing. One drawback, however, is the higher power consumption due to the backlight.
Pro points
- High contrast sharpness
- Good viewing angle stability
- Low response time
Drawbacks
- High power consumption
VA panel
The abbreviation stands for “Vertical Alignment”. This means that the liquid crystals move from a vertical to a horizontal alignment during commissioning. The contrast values are even superior to those of IPS panels. However, this technology has some disadvantages. The energy consumption is higher than that of IPS panels, and the screens are also not particularly heat-resistant. When touched with a finger, the image immediately turns dark.
Pro points
- Even higher contrast values than IPS panel
Drawbacks
- Higher energy consumption than IPS panels
- Less heat resistant
TN panel
The abbreviation stands for “Twisted Nematic”. Each pixel of such a panel consists of rod-shaped liquid crystals. The permanent backlighting is provided by LEDs. This type of panel is the undisputed first choice for gamers. When it comes to pure speed, TN panels are at the top because they have a response time of less than one millisecond. The high refresh rate of 240 hertz (Hz) is also only possible with this technology. In addition, this type of panel is very inexpensive. In terms of contrast and viewing angle stability, however, the TN variants cannot keep up with the VA panels.
Pro points
- Minimal response time
- Good refresh rate
- Inexpensive to buy
Drawbacks
- Lower viewing angle stability
- Slightly lower contrast values
What matters when buying
In addition to the panel type, there are a number of other criteria that can influence the purchase decision. These include display technology, resolution, refresh rate, ergonomics, weight and available interfaces.
Display technology
When it comes to display technology, a distinction is made between LCD and LED. In the “Liquid Crystal Display”, liquid crystals connected with a colour filter form the pixels. Each pixel is assigned to a transistor whose voltage regulates the position of the crystal and thus the colour. Fluorescent tubes located at the edges of the display provide the necessary illumination. These tubes are also the reason why the display is somewhat larger. With LED monitors, the pixels themselves light up. Each pixel consists of three light-emitting diodes in red, green and blue. The overall picture is therefore created by the principle of additive colour mixing. LED is the technology that has prevailed in current displays because the image builds up quickly and the monitors are both energy-saving and long-lasting.
Well-known brands
Philips | Dell | Samsung | BenQ | HP
Resolution
Resolution refers to the total number of pixels that make up the image. The more pixels the monitor has available, the more precisely and sharply it can display the picture. With 32-inch monitors, the user usually has a choice of three resolutions: Full HD, WQHD and UHD. Full HD refers to a resolution of 1,920 x 1,080 pixels and thus a total of two million pixels. That sounds like a lot, but for 32-inch monitors this resolution is basically already too low.
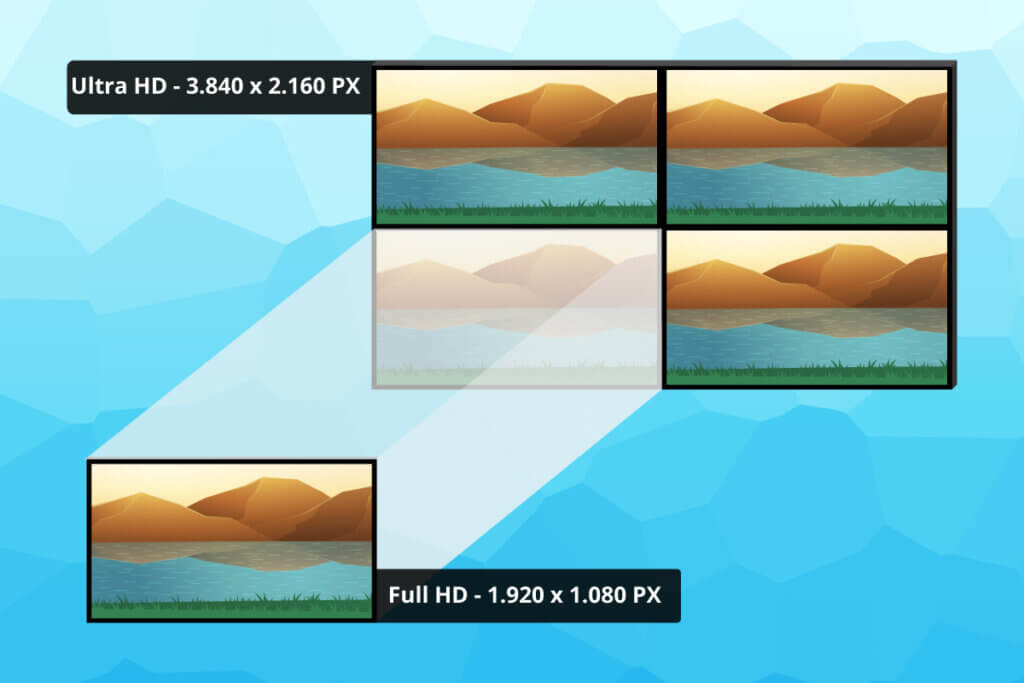
It is better to go for a monitor with WQHD (Wide Quad High Definition) in this size. WQHD offers four times the HD resolution, which is therefore 1.8 times higher than Full HD. Ultra High Definition (UHD), in turn, means a resolution of 3,840 x 2,160 pixels. In product tests, the terms UHD and 4K are often used synonymously, but from a technical point of view this is not quite correct, as the real 4K resolution only exists in cinemas. However, the difference in the number of pixels between UHD and 4K is comparatively small.
Frame rate
This refresh rate indicates how often per second the monitor can change the picture. This is of course more important for fast-paced computer games than for text editing. Standard 32-inch monitors offer a refresh rate of 60 hertz, which is sufficient for most applications. However, those who value fast gaming should choose a monitor with a higher frequency, such as 144 hertz. In addition, models with a refresh rate of 240 hertz are now available. However, this purchase only makes sense if you have a sufficiently powerful computer.
Pixel density
Another interesting feature of monitors is their pixel density. The common measure for this is dpi, or “dots per inch”. If two monitors of different sizes have the same resolution, the smaller one has the higher pixel density. This factor is less important when watching video material than when using the 32-inch monitor as a computer screen.

The Windows user interface, for example, is optimised for monitors with 96 dpi. On most current smartphones, this value is already significantly higher, which is why the image often appears smoother than on computer monitors. Of course, this is also due to the fact that the distance to the eyes is significantly smaller.
Only displays in the UHD class with extremely high pixel density can keep up with good smartphones in this respect. The term HiDPI has become established for this. Apple named the screens equipped with this technology Retina Display.
Response time
Response time refers to the interval that the monitor needs to change colours. The unit for this is milliseconds (ms). Values of ten milliseconds are already considered absolutely practical, only gamers will prefer monitors with a much lower response time, which on some devices is even as little as one millisecond. Some monitors even allow you to adjust the response time as needed, since the fastest possible response time usually comes at the expense of colour vibrancy and brightness.
What are the AMD Free Sync and NVIDIA G-Sync technologies all about?
The two manufacturers AMD and NVIDIA are the biggest competitors on the graphics card market. Both have developed their own image optimisation process. The functional principle is largely identical. It is based on synchronising the computer’s graphics card with the monitor’s refresh rate in order to avoid image errors such as judder. The difference, however, is that AMD has implemented its solution on the software side. The purchase of a special monitor is therefore not necessarily required. Nvidia’s G-Sync concept, on the other hand, is a hardware solution and works exclusively with the more expensive G-Sync monitors. While only the latest G-Sync monitors are compatible with Free Sync, conversely, the Free Sync solution can also be used with older G-Sync monitors.
Ergonomics
When it comes to ergonomics, the most important thing is whether the monitor can be adjusted in height and tilted forwards or backwards. This is important because the position of the monitor also affects the position of the person working with it.
A monitor that can be adjusted in height and tilt makes it possible to find a position that is optimal from an ergonomic point of view and thus prevents fatigue or even postural damage. Since some workplaces also involve standing, a monitor that can be adjusted as flexibly as possible is advantageous.

Weight
The weight of the monitor is particularly relevant if the user wants to mount it on the wall. For this purpose, there are mounts according to the so-called VESA standard. The product data sheet of the monitor contains a VESA marking, which can be used to find the appropriate wall mount if it is not already included in the scope of delivery.
Connections and interfaces
The available connections are important for connecting the 32-inch monitor to the PC and other office equipment. HDMI has long been the common standard for digital picture and sound transmission. Most current monitors have several such connections.
A DisplayPort also transmits sound and image digitally and even surpasses the HDMI connection in terms of resolution and frame rate. Since DisplayPort technology is the newer one, however, everyone should make sure to buy a 32-inch monitor with DisplayPort – not only those who have very high demands on colour reproduction. If the monitor has this connection, this ensures more sustainable compatibility with constantly improving standards such as 4K.
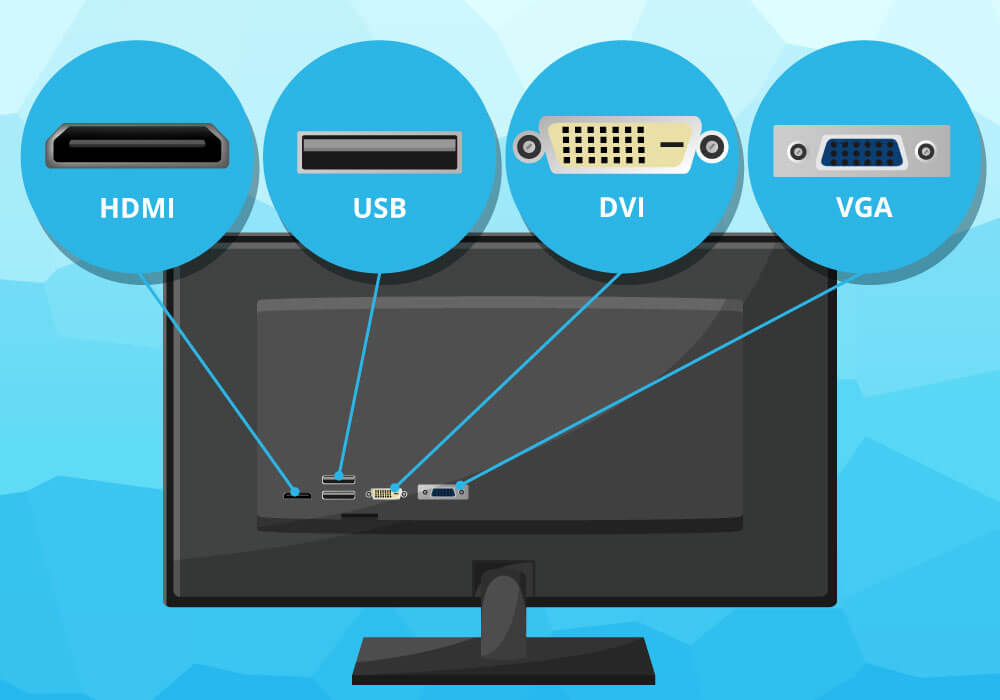
Many 32-inch monitors have USB ports to which the user can connect a keyboard, mouse or external storage media such as USB sticks. This is practical when the free USB ports available on the PC become scarce. Using the TOSLINK optical digital output, it is possible to output the sound via an external soundbar if the sound quality of the monitor’s built-in speakers is not sufficient or their volume is too low.
Older connections such as VGA, SCART or DVI are no longer up to date. Only those who own older devices such as beamers or VHS video recorders with these connections and want to use them with the new monitor still need such ports today.
Is a reflective or matt display better?
From an ergonomic point of view, a matt display is clearly preferable. With glossy display panels, unwanted reflections of light sources in the room often appear on the screen – sometimes even one’s own reflection, especially if reflective protective glass is installed in front of the actual panel. This is not only distracting, but can even lead to posture problems in the long run. After all, the user instinctively adopts postures that try to avoid these reflections even in the case of minor light reflections. Therefore, matt panels are clearly better suited for working at the screen. With reflective displays, films and computer games subjectively appear more colourful and contrasty, but this impression can sometimes lead to an unnatural-looking image.
Are curved displays still in keeping with the times?
Curved displays with a curved surface are particularly popular in the gamer scene. They give the user the feeling of being more immersed in the gameplay due to their better depth representation, for which the term immersion is commonly used. The monitor also has advantages when watching films and other television content because the contrast is better, especially at the edges of the picture. The disadvantage of the curved design, however, is that the optimal picture can only be seen from the central viewing position. These monitors are therefore unsuitable for film evenings with several friends. Moreover, the curved displays take up more space on the desk than the already large 32-inch monitors. Unlike with televisions, manufacturers have not stopped producing curved monitors.
What should be considered when placing a 32-inch monitor?
The user should place the monitor so that the view is directed slightly downwards. Under no circumstances should the top edge of the screen be at eye level. This is important not only for wider monitors, but also for higher 32-inch monitors. While the distance between the eyes and the screen is generally set at a minimum of 50 centimetres, this should be increased to 70 to 100 centimetres for the larger monitors. In order to be able to adopt the most relaxed posture possible, the screen should be placed straight in front of the user; windows and lighting should be parallel to the viewing direction. Incorrect positioning is often the cause of eye pain and headaches.













 19,081 reviews
19,081 reviews








