Satellite receiver purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- The most important facts in brief
- A satellite receiver converts digital broadcast signals received with a satellite dish into picture and sound.
- Compared to other reception technologies, DVB-S offers the best price-performance ratio and the fastest transmission.
- A receiver as an external set-top box offers advantages over the variant already built into the TV set.
- A satellite receiver should have a recording function and a smart card slot.
Satellite reception
With satellite reception, the television picture has travelled a very long way. Television stations beam the signal into geostationary orbit, which is 35,786 kilometres from the equator in space. In this orbit, there are television satellites that accompany the Earth at the same speed at which it rotates. This keeps the satellite always at the same point above the Earth.
The satellite beams the signal back to earth, where owners of a satellite receiver with a satellite antenna receive it. The most popular Astra satellites in Germany are located above the Democratic Republic of Congo. The Astra satellites cover approximately the area of Europe as a possible reception area.
Diversity thanks to satellite
The data transmission rate via broadcasting satellites is very high. Therefore, you can receive more than 1,500 national and international programmes via this type of reception.
Why the dish?
The distance covered by the satellite signal is very long. Therefore it arrives relatively weak. The task of the dish is to capture the signal and bundle it in a focal point. In this focal point is the LNB with an antenna and a frequency converter that enables the signal to be transported further through an antenna cable. The further away from Germany, the larger the satellite dish must be for good reception of the signal.
LNB
The abbreviation LNB, alternatively also LNC or LNBC, stands for the English term “Low Noise Block Converter”. This means something like “low-noise signal translator”. The LNB has a parabolic antenna for reception and a frequency converter for the conversion of the signal.
What is the task of the SAT receiver?
The satellite dish with the LNB is located outside the home and converts the signals from the satellite for transport in the antenna cable. The antenna cable ends in the flat in a receiver, which means “receiver” in German. Satellite receivers are either separate stand-alone devices or they are already built into the TV set. They convert the received digital data into picture and sound.
New television sets in particular are equipped with a DVB-S2 tuner, a multi-, a triple or even a quattro tuner. All these tuner types are suitable as satellite receivers for receiving the satellite signal. An external satellite receiver, on the other hand, is called a satellite receiver or set-top box, STB for short, which means “auxiliary device”.
A well-known manufacturer of satellite receivers is, for example, Technisat with the model series Technistar and Digit as well as the ISIO series, which even offers Smart TV functions with HbbTV. Other well-known manufacturers are Humax, Xoro, Edision and Kathrein.
What is DVB-S?
Since 2012, satellite television in German can only be received in digital form. The transmission standard DVB-S stands for this. The abbreviation stands for “Digital Video Broadcasting-Satellite”.
In the meantime, the successor standard DVB-S2 has become established. The quality of signal transmission with this standard is up to 30 percent better than with the predecessor standard. This is possible thanks to optimised coding, modulation and correction procedures. The result is visible: with a DVB-S2 receiver, the TV picture appears on the screen significantly faster and with higher resolution. The S2 standard was designed with the requirements for transmitting content in High Definition (HD) in mind.
Advantages of the satellite receiver
Television transmission via satellite signal is by no means the only method of digital television reception (DVB). Other standards of digital reception are:
- DVB-T/DVB-T2 (Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial): terrestrial television with a terrestrial antenna
- DVB-C/DVB-C2 (Digital Video Broadcasting-Cable): cable television via broadband cable
- IPTV (Internet Protocol Television): Internet television received via a set-top box or app and played back on a TV screen.
- WebTV/TV streaming: Transmission of live TV via the internet, received with a browser and played back on a PC or laptop
Satellite TV certainly offers advantages over all these variants and is the most widely used DVB transmission variant. A basic advantage of DVB-S is that the data transmission rate is very high and it does not require any infrastructure such as cable networks. The picture therefore reaches your screen more quickly and you do not need a cable socket. In addition, after the purchase costs for the satellite dish and receiver, there are no monthly fees or other follow-up costs.

DVB-S2 vs. DVB-C
Next to satellite reception, cable TV is the most widespread standard. Rented flats in particular usually offer the possibility of television reception via an existing cable connection, whereby the costs incurred for this are already integrated into the service charges. Users of the connection are usually tied to a cable provider who provides the services locally. For the use of the connection, the providers charge monthly costs of 15 to 25 euros.
Satellite reception has some advantages over DVB-C:
Advantages
- No running costs
- Greater variety of channels
- Foreign channels can also be received
- Less delay in transmission
- Excellent reception quality
Disadvantages
- Purchase and installation of dish necessary (sometimes not allowed in rented flats)
- Outages possible in bad weather
So if you are prepared to make the one-off investment of less than 100 euros for a satellite dish including LNB plus satellite receiver and are not afraid of its installation and space requirements, you will get away cheaper than with cable in the long term. If the user wants to receive private channels in HD, an HD+ smart card must be purchased monthly for about 60 euros per year. Public broadcasters provide their programmes free-to-air in HD via satellite.
A clear shortcoming with live programmes is the slower transmission speed of DVB-C compared to satellite reception. In the context of the 2016 European Football Championship, the IT trade magazine c’t examined the delays of the various reception standards with which they output picture and sound on the television. Cable reception and IPTV lagged significantly behind in transmission with a time delay of 4 to 11 seconds. Only web TV fared even worse with a time delay of 30 to 56 seconds, varying depending on the streaming provider. Satellite TV in DVB-S2 reception in standard definition (SD) was ahead in the comparison with only about one second delay.
DVB-S2 vs. DVB-T2
Television reception via an earth-bound antenna (DVB-T) offers the advantage that the user does not need a large dish, but only a small, compact antenna to receive the signal. Apart from the acquisition costs for the antenna and the corresponding receiver, there are no follow-up costs for DVB-T2. In contrast to DVB-S, with terrestrial reception Mobile TV, i.e. reception of the signal via mobile antennas, is possible at speeds of up to 200 km/h. The disadvantage of this variant, however, is that it requires a small, compact antenna.
The disadvantage of this variant, however, is a limited programme variety, which is a consequence of the low transmission bandwidth. Although the new DVB-T2 transmission standard offers more than 40 different channels in HD quality, there are additional costs for receiving the private channels in HD.
Overall, the DVB-S standard offers numerous advantages over DVB-T2 with only a few disadvantages:
Advantages
- Greater variety of channels
- Foreign stations can also be received
- Slightly higher transmission speed
- Best picture and sound quality
- No dependence on transmission towers and broadcasting areas
Disadvantages
- Mobile reception not possible
- Dish requires more space and installation effort than antenna
- Weather-related outages possible
DVB-S2 vs. IPTV
The technical standard of IPTV itself already has some disadvantages compared to satellite reception. One is dependent on a stable internet connection with a good data transmission rate. If the bandwidth is poor, picture interference and drop-outs occur. For some regions in Germany, this type of reception is therefore out of the question. Even with good and stable data transmission, the time delays in picture and sound transmission are significantly higher than with satellite television.
Switching between channels takes longer with IPTV than with DVB-S. Since it is an internet-based service, we can also cite concerns about data protection. The viewing behaviour of an IPTV user is clearly traceable and can be evaluated by the provider itself or by third parties.
Overall, the advantages of satellite reception outweigh those of IPTV:
Advantages
- Hardly any time delay during transmission
- Fast channel change
- Best picture and sound quality
- No monthly costs
- No dependence on internet access
- No dependence on a provider
- No contract commitments and minimum terms
- Viewer behaviour cannot be analysed in detail
Disadvantages
- No on-demand content or TV archives
- No reception via computer, smartphone or tablet possible
- Higher purchase and installation costs
- Weather-related outages possible
Why a set-top box and not an integrated DVB-S2 tuner?
Why should you use an external satellite receiver as a set-top box when TV sets with integrated DVB-S2 tuners have long been available on the market? The advantages of integrated receivers are obvious:
- Compact combination of the devices
- Only one remote control for both components
- Less cable clutter
What may sound practical and sensible at first, however, harbours one or two pitfalls. A separate satellite receiver is preferable in many respects.

Is it a SAT receiver at all?
If a TV set has an integrated receiver, this does not mean that the receiver is also suitable for receiving satellite TV. Some models are only equipped with receiver modules for DVB-T or DVB-C. You should also be careful with the term dual tuner. Two types of reception do not automatically mean that the device is DVB-S-capable. Therefore, always look for the specific indication “DVB-S” or “DVB-S2”.

Purchase price
Televisions with an integrated receiver are usually more expensive than models that do not have this component. In case of doubt, it is therefore worth comparing the price of an all-in-one set with that of a conventional TV set plus the external satellite receiver. External receivers are still much more in demand than integrated models and are therefore produced in larger numbers. As a result, high-quality receivers can be purchased relatively cheaply. If you still have a functioning TV set anyway and only want to “upgrade” satellite reception, you should go for the external receiver version anyway.

Is it “recordable”?
Owners of a satellite receiver no longer need a video recorder or an external recording device, because today’s receivers are generally equipped with a recording function. The programmes are already available in digital form through the reception path, which makes it easy to store and flexibly retrieve the data. A TV set with an integrated receiver, on the other hand, makes this possible only if it has the feature “PVR-ready” (Personal Video Recording) or “DVR” (Digital Video Recording).

Compatibility problems
Many manufacturers of TV sets with integrated satellite receivers allow the recording of programmes via an external hard disk, but they cause problems when importing and playing back the recorded files. This can easily lead to compatibility problems with other devices. An external receiver has numerous interfaces that make it easy to transfer the recorded content to various third-party devices.

In the event of a defect
Digital receivers and DVB-S tuners integrated in televisions are complex technical devices that can be affected by defects. The integrated tuners in particular are more prone to malfunctions due to their compact design. One disadvantage of the built-in tuner: a defect can affect both components at the same time. If only one component is defective, repair and, if necessary, replacement is much more difficult, time-consuming and thus more expensive than with a separate satellite receiver. In the event of a warranty claim, it is also easier to send in a small receiver than a large flat-screen TV.

WLAN extension
If your satellite receiver does not have a WLAN function, you can easily upgrade it with a WLAN stick to make it Internet-capable. You simply connect such a stick via the USB port of the receiver. As with a Smart TV, you can then surf the Internet with the TV. To make it easier to enter letters and numbers in the browser, it is also advisable to connect a keyboard. This also requires a USB connection.
What types of satellite receivers are there?
Satellite receivers are available in many different versions with different features. You should know these in order to make an informed purchase decision and to understand why there are receivers in different price ranges.
Receivers with hard disk
An external satellite receiver can be equipped with an integrated hard disk. This is useful if you intend to record programmes and films with the receiver. However, the hard disk alone is not sufficient. The receiver must also have a recording function. This is called a “Personal Video Recorder” (PVR) or “Digital Video Recorder” (DVR).

Depending on the capacity of the hard disk, the costs for such a receiver are considerably higher than for a model without a hard disk. If you can do without a recording function or want to use external storage media, you can save money.
Receivers without a hard disk
A set-top box that is not equipped with a hard disk cannot store files itself, but this does not mean that you cannot make recordings with the device in principle. If the set-top box is PVR- or DVR-ready, it has the technical requirements for recording programmes and films. In this case, however, you need an additional external storage medium to store the files, i.e. an external hard disk or a USB stick, which you connect to the receiver via the USB socket.

The advantages of this spartan variant are obvious: a lower purchase price and full flexibility in choosing the type and capacity of the storage medium. The recordings can also be played back via another receiver, and in the event of a defect, it is not necessary to repair the entire unit; it is sufficient to replace the external memory. If you want to connect external storage media to the receiver, however, you should find out in advance whether the receiver is compatible with them. Since recording in HD quality takes up quite a bit of storage space, the storage capacity of the external hard disk should not be too small.
Multituner
A pure satellite receiver only allows reception of digital broadcast signals via the DVB-S transmission standard. However, many receivers are equipped with a multi-tuner. This means that they can process several transmission standards. There are different types of multi-tuners:
- Dual Tuner: The receiver is able to process two signal ranges, for example DVB-S and DVB-T.
- Triple tuner: A triple tuner processes the three reception standards DVB-S, DVB-T and DVB-C.
- Quattro Tuner: In addition to DVB-S, DVB-T and DVB-C, these receivers also support reception of Internet television (IPTV).
Of course, the price of the devices increases with the number of reception options offered. So if you are satisfied with just satellite reception, you do not need a receiver with an integrated multi-tuner.
Linux receivers
Receivers with Linux operating systems are considerably more expensive than ordinary satellite receivers, but they shine with maximum flexibility and adaptability. The digital all-rounders not only serve to receive and decode broadcast signals, but also function as a true multimedia centre. Via the operating system, you can install further plug-ins that considerably expand the functions of the satellite receiver.
A Linux receiver can be integrated into the home network via LAN or WLAN. With the appropriate software, you can then configure the receiver on the PC. The plug-ins enable, for example
- the display of additional information on channels,
- automatic volume control,
- the transmission of screen contents to mobile devices,
- the installation of games,
- the retrieval of news or weather data,
- watching YouTube videos,
- installing video editing programmes, and
- accessing broadcasters’ media libraries.
The possibilities are very diverse and also include, for example, the individualisation of channel logos, menus and background images. Operation, however, requires some time of familiarisation and an advanced technical understanding.
Equipment and connections of the receiver
When buying a new satellite receiver, you should not only pay attention to the right technology and the price. Important connection options should not be missing. We also show you which features you can use to compare receivers and how to find the right receiver for your needs.
Connections
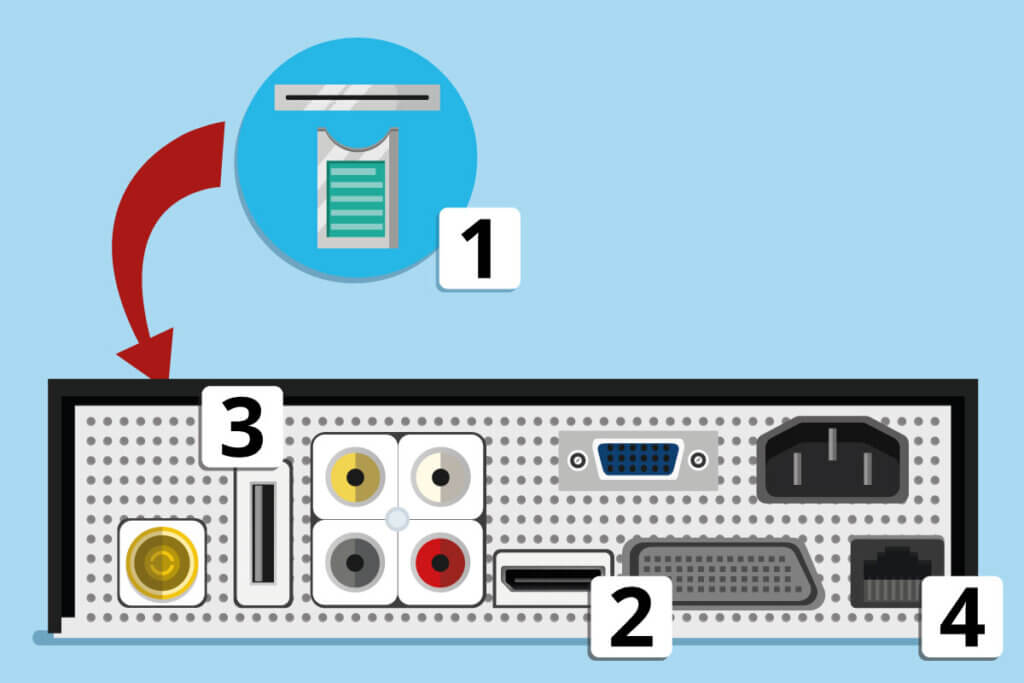
- CI+ slot (Common Interface card slot) and Smartcard slot: Input of CI modules, mostly in the form of prepaid cards for paid TV programmes.
- HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface): Cable connection for HDMI cable that transmits picture and sound information simultaneously in the best quality.
- USB (Universal Serial Bus) and eSATA (External Serial Advanced Technology Attatchment): Input for external storage media such as hard disks and USB sticks or connection for keyboards.
- LAN and WLAN: For integrating the receiver into the home network via LAN cable or wirelessly.
HD compatibility
Every DVB-S2-capable HDTV satellite receiver is capable of decoding and reproducing content in HD. When buying a receiver, look for the specification HD-Ready or HDTV-Receiver. So far, however, only public broadcasters such as ARD and ZDF broadcast their content free of charge in high-definition format.
Private broadcasters, on the other hand, do not offer their content in HD free of charge. If you also want to enjoy programmes from private broadcasters in HD with your satellite receiver, you must purchase an HD+ card and insert it into the CI+ slot of the receiver. It costs about 60 euros per year.
UHD satellite receivers
In addition to HD receivers, there are even satellite receivers that are able to play content in UHD, also called 4K. It should be noted, however, that so far only a few TV contents are offered in 4K. Only pay-TV providers such as Sky already offer UHD channels.
Another way to enjoy TV in HD quality is freenet TV. The offer includes twenty private and twenty free-to-air channels. Originally, this option was limited to DVB-T2 reception, but now there is also a corresponding module for satellite receivers for 5.75 euros per month. You simply insert it into the CI+ slot of the receiver.
Twin tuner
The twin tuner is not to be confused with the dual tuner, which supports two different types of transmission. Rather, a twin tuner allows you to watch one channel via one type of reception, for example DVB-S2, and at the same time record another programme via the same reception path. This is possible thanks to two separate reception units integrated in the twin receiver.
However, receivers that support more than one type of reception are also available with the Twin concept:
- Twin-Dual-Tuner: reception and simultaneous recording of two transmission types, for example DVB-C and DVB-S2.
- Twin Triple Tuner: reception and simultaneous recording of the three signal ranges DVB-S2, DVB-T2 and DVB-C
- Twin-quattro tuner: reception and simultaneous recording of DVB-S2, DVB-T2, DVB-C and IPTV
For the majority of users, however, it will be completely satisfactory to be able to watch one programme and record another at the same time. For this purpose, a pure Twin-Sat receiver without further reception options is sufficient.
Recording and Time Shift
If the receiver has “PVR” (Personal Video Recording) or “DVR” (Digital Video Recording), it is able to record content and store it as a file on an internal hard disk or an external storage medium, if available. Pressing the record key on the remote control is sufficient to record the live programme in parallel. The recording of future programmes can be programmed via the digital programme preview with just a few entries.
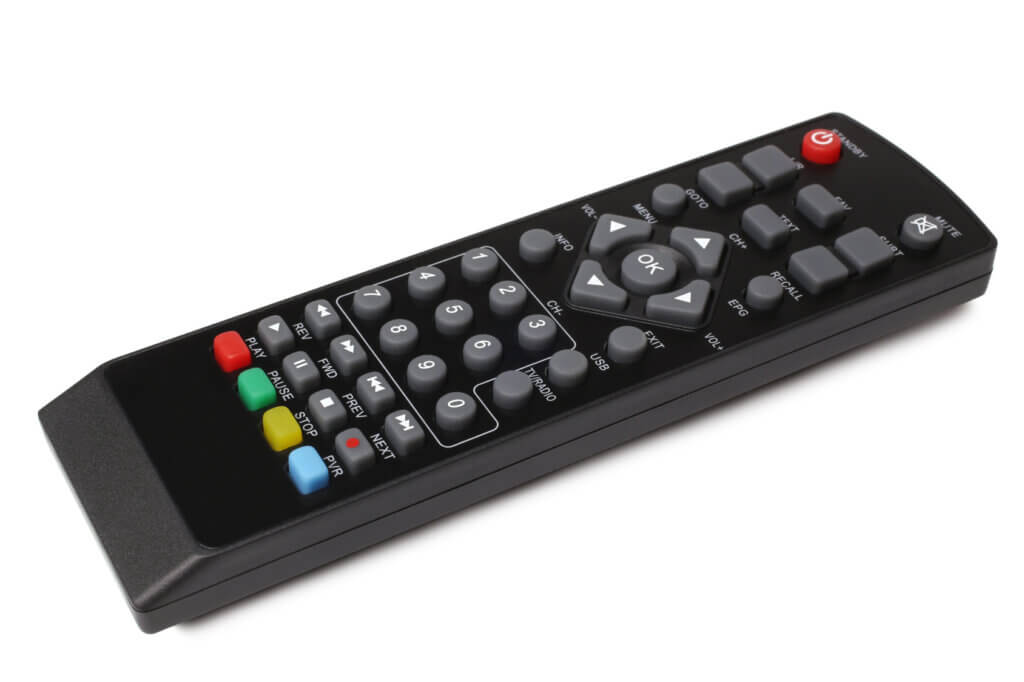

Recording content also makes it possible to use the so-called time-shift function later. The remote control of a satellite receiver usually has a play/pause button with which you can pause the live programme or a recording at any time and let it continue playing at a desired time. Pressing the pause button during a linear TV broadcast stops the programme playback, but the receiver records all subsequent content for time-shifted playback.
Tip
Long commercial breaks can be a real nuisance when watching a film in the evening. If you activate the Time Shift function at the beginning of the film transmission, you can still do other things without any problems and only start playback an hour later. You can then simply skip annoying commercial breaks.
Connecting and setting up
Connecting a satellite receiver does not require extensive technical knowledge and is child’s play even for non-professionals. In most cases, there are only three simple steps you need to take to connect the receiver. The sequence plays an important role: For safety reasons, you should only connect the receiver to the mains in the last step.
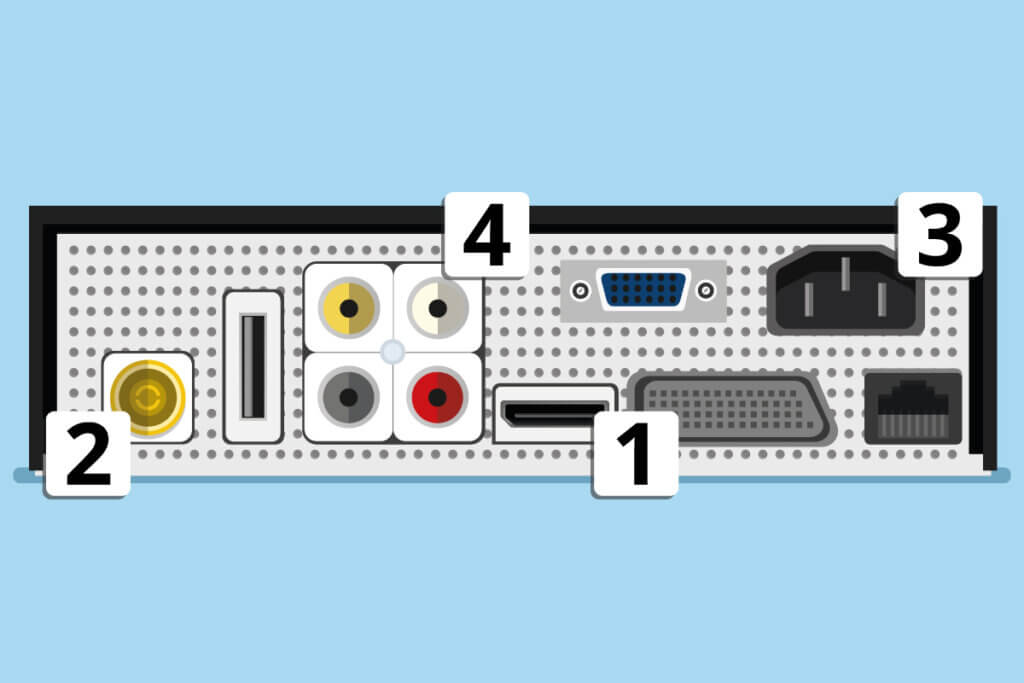
- Connect the HDMI cable (alternatively the Scart cable for older sets) that connects the receiver to the TV set.
- Connect the coaxial cable (antenna cable) that connects the antenna input of the receiver to the satellite dish or the wall socket via a screw thread.
- Plug the mains plug into the socket for power supply.
- Optionally, connect the sound system via cinch connections.
Setting the receiver
After connecting the receiver, the next step is to search for channels. Modern receivers do this automatically as far as possible. To do this, first open the menu with the remote control. This should show a sub-item for channel search, sometimes also called station search or programme search. After selecting the relevant menu item, the automatic channel search should start. You can set the channel order manually after the search is complete. The menu also offers setting options for picture and sound.













 105 reviews
105 reviews


