Sand filter pump purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
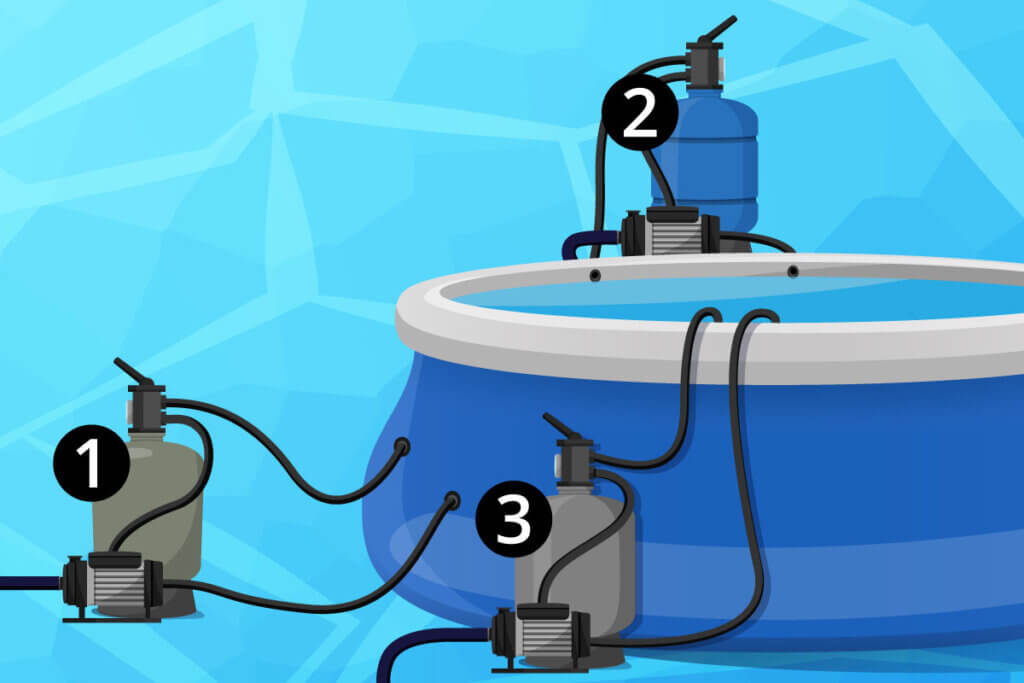
- Sand filters clean pool water by means of circulation.
- The three main components are a multi-way valve, a pool pump and a filter vessel.
- The water is forced through a filter filled with sand. Dirt particles are thus sieved out of the water.
- In pools, sand filters are installed between the extractor and the inlet nozzle.
- Low flow rates and large pool volumes increase the running time.
What are filter systems used for?
Filter systems, sometimes also called pool filter systems, enable smooth bathing. They circulate the bathing water and force it through a filter. In this way, they ensure that it always remains clean. Foreign matter such as insects, leaves, dust and skin residues are retained in the filter, so that clean, clear water is returned to the pool, the prerequisite for bathing pleasure that is not harmful to health.
What are the differences between cartridge and sand filters?
When you set up a swimming pool, the question also arises as to what kind of filter system you need to keep the water clean and hygienically safe. Although many pools already come with filter systems, these are often not sufficiently effective and only remove coarse impurities such as blades of grass or leaves. Basically, a distinction must be made between cartridge and sand filters. The choice between the two variants depends mainly on the size of the pool and the installation site.
Cartridge filter
Contaminants are quickly and efficiently removed from the water by means of a cartridge filter. Whether indoors or outdoors, they are especially suitable for pools that do not get too many dirt particles that would require quick cleaning or changing of the filter cartridge. Cartridge filters are cheap to buy: inexpensive models are available for as little as 40 euros.
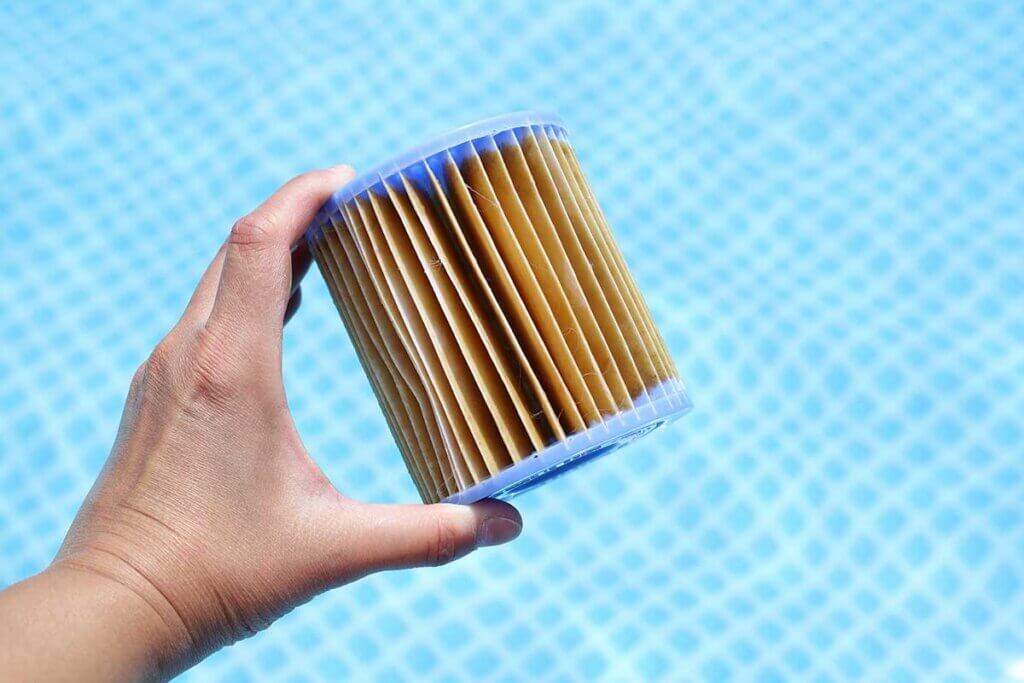

The disadvantage is that the paper cartridge, which is connected upstream of the pump, has to be replaced regularly as soon as it is full, which causes follow-up costs and makes regular operation expensive. Replacement filters cost an average of 5 to 10 euros, although some models can be more expensive. Although in some cases it is possible to clean cartridge filters by lightly hosing them down with a garden hose, cleaning does not always bring the desired success, as dirt remains in the filter paper. In addition, it can be damaged, so that you have to replace it directly in this case.
Cartridge filters are ideal for keeping water clean in small above-ground pools or in a paddling pool. This is because: cartridge pool filters are generally less efficient than models that work with a sand filter. It therefore takes longer to circulate the entire pool contents. If the system is too small, it has to run for a very long time, which results in high electricity costs. The other possibility is that the system simply does not manage to clean the entire water volume fast enough, which is why the water looks dirty and bathing in it seems unattractive.
Always pay attention to the flow rates in the manufacturer’s specifications. These provide information about how much water can be cleaned in an hour. It is therefore not possible to make a general statement about the maximum pool size that can be cleaned with a cartridge filter. For small pools, a model with a cartridge filter is sufficient. Many manufacturers recommend using their models with a filling capacity between 5,000 and 8,000 litres. For pools with larger water volumes, it is definitely worth investing in a sand filter. If the pool contains a lot of coarse dirt particles, for example from insects, the paper filters will quickly become clogged. In this case, a sand filter is also the better alternative.
Pro points
- Low purchase price
- Ideal for small indoor pools
Drawbacks
- Quickly clogged by large dirt particles
- High follow-up costs due to replacement cartridges
- Suitable for large amounts of water
- Less efficient than sand filters
- No use of flocculants possible
Sand filter
In sand filters, a filter bowl filled with special sand replaces the paper filter cartridge. The sand should have a grain size of about 0.5 to 0.8 millimetres. This value depends on the specific sand filter model, the amount of water and the degree of contamination of the water. The water is forced through the filter bowl and thus through the sand by means of a water pump at high pressure. During this cleaning process, suspended particles are filtered out of the water: they remain suspended in the sand; the water is then returned to the pool.
The quartz sand can be cleaned by backwashing and then reused. The disadvantage is that freeing the filter sand from dirt and suspended particles takes longer than simply replacing a filter cartridge. During this process, the dirt is “backwashed” into the drain to maintain the sand’s high filtration performance. This process takes a few minutes and should be carried out about once a week, depending on the degree of contamination. Scheduled regularly, however, this maintenance is not an overly big problem.
A sand filter usually costs over 100 euros and thus more than a cartridge filter. However, the higher purchase price pays for itself quite quickly with regular use: since no filter cartridges have to be bought again, the follow-up costs are reduced. The filter sand only needs to be replaced about every two to three years, when backwashing no longer leads to the desired cleaning performance. In addition, the cost of purchasing 25 litres of filter sand is not particularly high at 8 to 25 euros. In the long run, the use of a sand filter system is therefore more cost-effective.
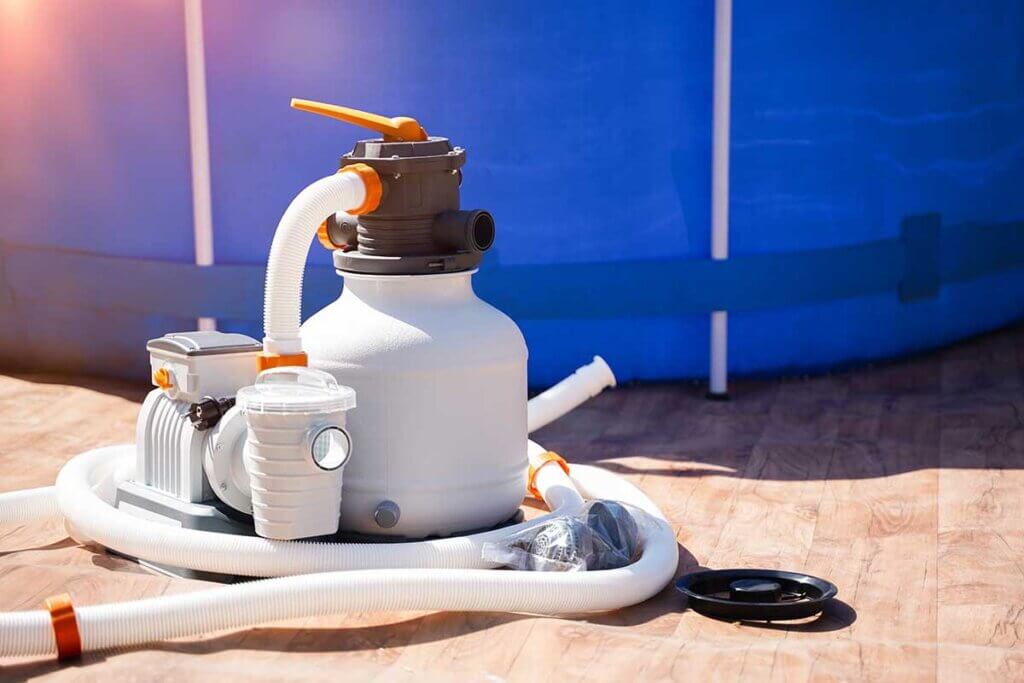

Due to their high cleaning performance, sand filter systems are particularly suitable for pools with large amounts of water, such as steel-walled pools. Sand filter systems are also advantageous for outdoor pools with a high dirt input, for example, if the environment is sandy or a particularly large number of insects are brought in.
Sand filter systems are often bought as a replacement for an existing cartridge filter system if the users are dissatisfied with the cleaning performance of the exchangeable filter: Sand filter systems offer a filtering power that could not be achieved with a cartridge system. The larger the pool, the more sensible it is to use a sand filter.
Pro points
- Ideal for pools with large amounts of water
- More powerful and efficient than cartridge filters Higher cleaning effort
- Change of filter medium less often necessary
- Lower follow-up costs
- Often operation with filter glass or balls possible
- Flocculants can be used
Drawbacks
- More expensive
Criteria for choosing a model
When choosing a suitable sand filter system, purchase criteria such as filter performance, power consumption and hose connections play a role.
Flow rate
The flow rate of a sand filter system is always related to a unit of time. It is given in cubic metres per hour (m³/h) or litres per hour (l/h). One cubic metre corresponds to 1,000 litres. For example, if a filter has a capacity of six cubic metres, 6,000 litres can be circulated and filtered per hour.
If the flow rate is too low, the pump has to run continuously, which results in high electricity consumption. In the worst case, not even constant filter operation guarantees sufficiently good water quality. If the sand filter system is oversized, this will not have a negative impact on the water quality, but the electricity costs will be higher than they should be. When deciding on a purchase, therefore, always pay attention to the filter capacity per hour and the maximum water volume.
In addition, a distinction must be made between two values:
- on the one hand, the calculated maximum possible flow rate without filter material and delivery head (gross)
- on the other hand, the actually achievable delivery rate with filter material and assumed delivery head (net).
When making a purchase decision, look out for advertising claims that use the net capacity in order to look better in the comparison.
The editors of the pool accessories shop Poolpanda explain in a YouTube video that the pump should circulate at least one fifth of the water content per hour. If your pool holds a water volume of 20,000 litres, the filter system should accordingly be able to pump at least 4,000 litres net per hour. More powerful pumps with a 4:1, 3:1 or 2:1 ratio are possible. However, these consume more electricity in continuous operation and are potentially more expensive to purchase.
Power consumption
The power – given in watts – provides information about the amount of electricity consumed during continuous operation. If, for example, you choose an economical model with an output of 300 watts, 0.3 kilowatt hours (kWh) will be added to the electricity meter for one hour of continuous operation.
For a large pool, however, you should not choose a model that is too weak. Otherwise, you will have to run the pump longer until the entire volume of water has been filtered once. This in turn negates the potential savings of lower power consumption. However, low power consumption does not mean a reduced performance balance. Therefore, pay close attention to the flow rate.

Boiler size
The boiler size is a decisive factor for the efficiency of the filter system. Diameters of 25 to 40 centimetres are common on the market. The filter material – usually quartz sand – must be purchased separately. Depending on the boiler volume, between 10 and 25 kilograms of sand are required; the recommended grain size varies from model to model. The range is usually between 0.5 and 1.2 millimetres.
Delivery head
The delivery head, sometimes also referred to as the water column, is a measure of the back pressure that the pump can overcome. This can vary due to differences in height, the distance to be covered and the resistance of the hose lines. The higher the back pressure, the lower the circulation capacity. The higher the specified value, the longer the distance and the greater the difference in altitude that the sand filter can cover without losing circulation capacity. The manufacturer’s specifications usually refer to the amount of water filtered in cubic metres per hour with a water column of six or eight metres.
Non-self-priming or self-priming?
If you are faced with the choice between a non-self-priming and a self-priming model, there is a price difference and a technical difference. The non-self-priming models are cheaper and more compact. With them, the water runs into the filter by gravity alone and is reintroduced into the water with the help of the pump. This only works if the filter system is located next to the pool, the water flows off to the side and is also reintroduced. However, if the hoses for the water inlet and outlet are routed over the edge of the pool or if the pump is located above the water level, a self-priming pump system is required. Otherwise, the suction and pressure effect is too low to be able to circulate the water.
Valve
The valve is used to regulate the various functions of the filter system. Depending on the number of functions, we speak of four- to seven-way valves. The classic four settings are
- Filtering,
- Rinsing (for removing suspended matter),
- Backwash (for filter cleaning) and
- Winterproof (valves open to relieve seals).
Some models also have programme functions such as
- Closed,
- Circulate (without filtering) and
- Empty.
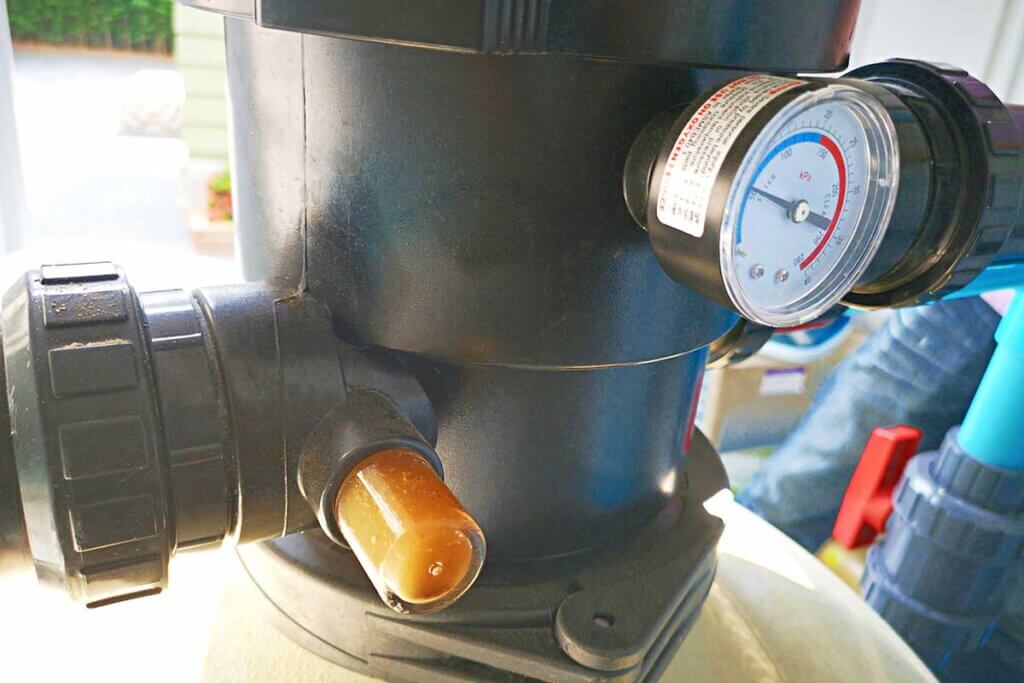
Pressure gauge
You can see if the pump is working properly by looking at the pressure gauge: If the pressure displayed is significantly above normal, the filter, in this case the boiler, is probably blocked by large accumulations of dirt. At the latest now it is time for cleaning by backwashing.
Hose connections
The most common connections are for hoses with a diameter of 32 or 38 millimetres. Many filter models have both connection sizes. It is annoying when the pump does not fit the hose. In most cases, however, the problem can be solved without much effort by using an adapter.
Connection options for skimmers and vacuum cleaners
Skimmers are used to remove the dirt floating on the water surface. They are available as built-in and surface versions. The former is similar to the drains in outdoor and indoor pools at the edge of the pool and is common, for example, in masonry swimming pools. The latter is attached to the edge of the pool and, as its name suggests, floats on the surface of the water. Both make use of the suction effect of the pump. Foreign bodies floating on the surface, such as leaves, are automatically sucked in. You can easily dispose of these entries by removing the collection basket.
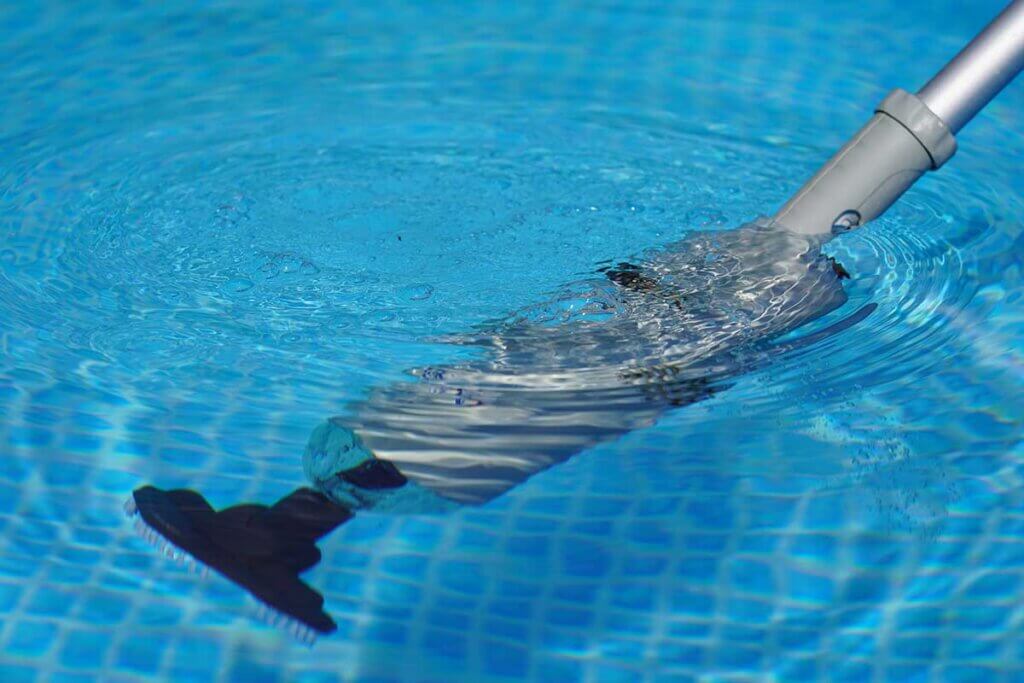

The principle of a hoover is similar to that of a hoover: the nozzle is positioned at the bottom of the pool and the hose is connected to the skimmer by means of an adapter. This creates a vacuum that sucks in foreign bodies at the bottom of the pool. The dirt trap of the skimmer must also be emptied after some time.
Connection option for UV filter
Some models allow the integration of a UV filter. For cleaning, the water is irradiated with UV-C light and thus made germ-free. Due to the high energy, UV radiation can render bacteria, viruses and many spores harmless. This means that the addition of chlorine or active oxygen can be significantly reduced or at times becomes superfluous.
Volume
If you operate a sand filter system in the garden, the issue of noise can quickly take on a major role; after all, you don’t want to risk any trouble with the neighbours. This is especially true at quiet times such as during the lunch break, after 10 p.m. or on Sundays. As a rule of thumb, you could say: the more wattage the device has, the louder it is. Although there are also powerful, low-noise units in the professional sector, these are usually prohibitively expensive for private users. The differences in volume are considerable: units can be between 40 and 75 decibels loud.
Are there alternatives to sand as a filter medium?
An alternative to filter sand is filter glass. It is made from the production residues of the glass industry and is therefore environmentally friendly. One advantage over filter sand is that a biofilm does not form so quickly on the surface of the glass. Compared to filter sand, this allows for a longer service life of the glass filter medium before it has to be replaced. In addition, the efficiency is higher due to the rough surfaces. The only disadvantage is the higher purchase price. However, when you consider that filter glass only needs to be replaced every three years or less, this factor is not too significant.
Some models can also be operated with so-called filter balls. These are made of polyethylene (PE), absorb a lot of dirt, have a high filtering capacity and replace the filter sand. Once saturation is reached, they can usually be cleaned in the washing machine. In addition, they can be recycled at the end of their service life. Be sure to read the instructions for use of the sand filter system to find out whether filter balls can be used with your filter system. In general, it is not possible to use flocculants with filter balls, as this would clog the filter medium. In addition, backwashing does not work, so the tank has to be cleaned by hand.
Do I have to clean pool water chemically in addition?
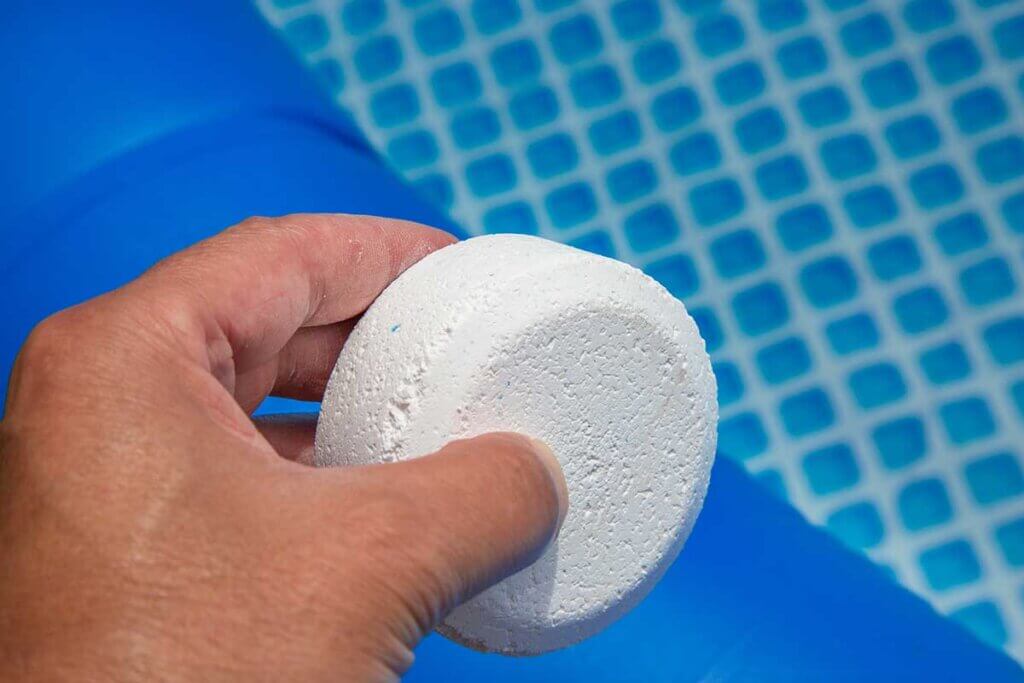
In addition to cleaning the dirt with a sand filter, it is advisable to chemically clean the water from time to time. The most common method is to add chlorine tablets. They are cheap and work for a long time. Alternatively, chlorine-free products based on hydrogen peroxide – also known as active oxygen – can be used. This is the more environmentally friendly option, but it involves more work: the chlorine-free agent is not as effective and must be applied more frequently.

What role does the pH value of the water in the pool play?
The pH value indicates whether the water in the pool is too acidic or too alkaline. Neutral is a pH value of 7. If the pH value of the water is between 6.8 and 7.4, you do not need to do anything. If the reading is below this range, the water is too acidic and can damage metal components of the pool, such as a ladder. pH readings above 7.4 indicate water that is too alkaline and can cause skin and eye irritation. The more the measurement deviates from the ideal value, the greater the respective effect. Water care products and chemicals also usually develop their ideal effect in this range. Pay attention to the instructions for use. pH meters and pool testers offer a convenient way to determine the pH value.
What can flocculants be used for in sand filters?
Coarse particles get stuck in the sand during the filtering process. Very small particles that are smaller than the sand grains cannot be filtered in normal operation and end up back in the pool. This usually does not represent a loss of functionality. If there is a desire to increase the filter accuracy even further, flocculant can be added to the filter sand. The advantage is that very small particles, such as dust, clump together from then on, get stuck in the sand and can be filtered out just like the coarse dirt. The result is even clearer bathing water.
How long should a sand filter system run per day?
There is no general answer to this question. Rather, it depends on the pool size and the frequency of use. As a rule of thumb, a pool pump with sand filter should run eight hours a day. During this period, the water must have flowed completely through the filter twice so that it can develop an optimal cleaning effect. It is also advisable not to run the pump for eight hours at a time, but to divide the operating time into two to three blocks per day. Therefore, make sure that the flow rate matches the amount of water.


















 2,006 reviews
2,006 reviews






