Exercise bike purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- Exercise bikes simulate the motion of cycling.
- In addition to the classic bicycle ergometer, there are also recumbent ergometers that are easy on the back, professional spinning bikes, rowing ergometers for indoor rowing and folding models.
- The machines are not only used for private purposes, but also for medical purposes, such as performance diagnostics or rehabilitation.
- Whether you are a senior citizen, a beginner or a competitive athlete, with an ergometer you can increase your fitness in a way that is measurable and easy on your joints, regardless of the weather.
- In addition to heart rate, ergometers also measure and record speed, distance covered and calories burned.
The training bike for the living room
After a long break from sports, you’ve decided to get back into training and get your stamina going? When you look at the scales, you are shocked to see that the weeks of inactivity have made themselves felt? Or perhaps you are so busy at work or with your family that you can’t invest much time in a sports club or gym? To maintain the health of your body, regular exercise is essential. Cycling is generally considered one of the healthiest sports that is easy on the joints. However, it is not possible to cycle in all weather conditions. Moreover, some cyclists do not have the opportunity to ride on a suitable track. The remedy is an ergometer, also known as a bicycle ergometer, indoor bicycle or fitness bike, which is similar to a bicycle but designed for indoor use. With this weather-independent alternative to cycling, the popular excuse of rainy weather also loses its validity.
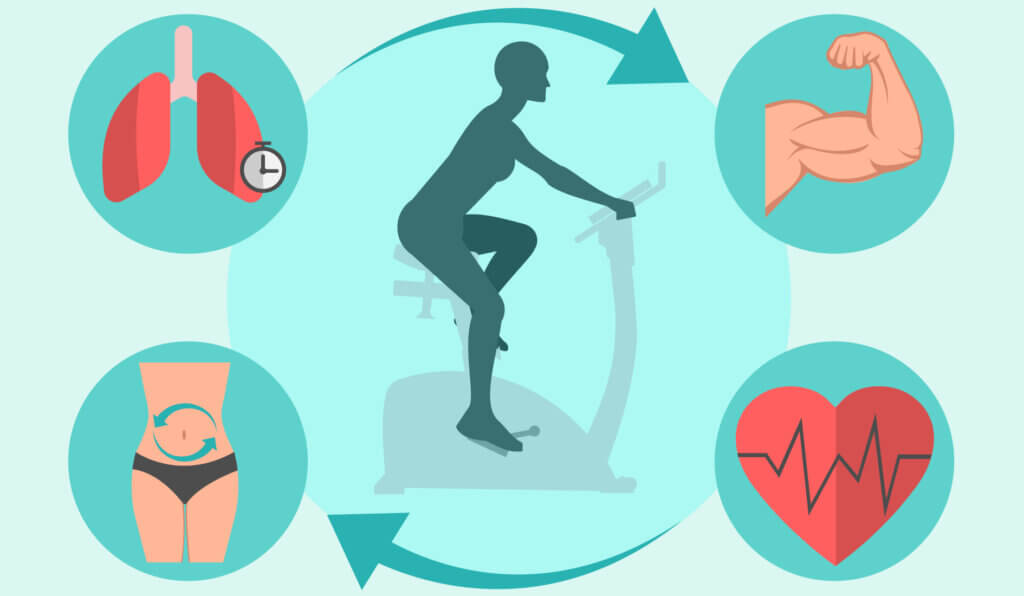
Fitter, slimmer, healthier: the training goals
Be it targeted fat loss, a sporty balance to everyday life or a fit cardiovascular system – with an ergometer, users can start at different training levels depending on their personal condition and goals. Because it offers an intensive workout that can be individually adjusted, increased and measured, an indoor bike is ideal as a piece of sports equipment for beginners, returners and fitness enthusiasts. Just 30 minutes three days a week is enough to get the circulation going, stimulate the metabolism, strengthen the muscles and optimise endurance. Regular training strengthens the heart muscles, which increases the stroke volume and thus the oxygen intake. At the same time, the resting pulse rate drops and blood pressure stabilises. Another bonus: Through cardio training, athletes increase their lung capacity. This is particularly beneficial for asthmatics.
The physical exercise leads to more vitality, higher performance, better body awareness and a strengthened immune system. Since the ergometer mainly uses the legs, the calorie consumption is lower than with other endurance sports such as jogging, but diligent exercisers burn up to 500 calories per hour. By boosting the metabolism, the calories are burned better and faster, so that the excess pounds fall off quickly. The gentle mobilisation of the knee and hip joints also helps to switch off after a stressful day. Thus, the use has a positive effect on body and mind.
Measurably better training: The advantages of ergometers
Regardless of age, fitness level and training goal, ergometers offer numerous advantages over ordinary bicycles, but also treadmills and other sports equipment for cardio training. Exercising on a bicycle ergometer is an easy, comfortable and joint-friendly way to complete your daily or weekly fitness session. Thanks to the numerous programmes and the adjustable resistance levels, users can determine their training individually and prevent overloading. This makes it possible for beginners, among others, to get off to a gentle start.
Professional athletes, seniors and people with certain pre-existing conditions benefit from the permanent control option. With a performance display that measures the pulse, calorie consumption and the distance covered, users can check exactly how fit their body is. At the same time, indoor bikes make it possible to set goals, which increases motivation. For this, interested people who do not have the luxury of a fitness studio available around the clock do not even have to rely on opening hours, as it is possible to accommodate an ergometer in one’s own four walls due to its limited space. Thus, a bicycle ergometer is always available. While exercising, it is even possible to listen to music or watch a film.
Although users save the fee for the gym, the purchase of a fitness bike is associated with a higher cost, at least once. Moreover, the workout is not a full-body workout, but mainly works the leg and pomus muscles. Because it is performed in a seated position, it is comparatively one-sided and not an adequate workout for people who work primarily at a desk. Nevertheless, the advantages clearly outweigh the disadvantages, as the following table illustrates:
Pro Points
- Strengthening of the muscles
- Strengthening of the cardiovascular system
- Increased endurance
- Gentle on the joints
- Possibility to control the body’s performance
- Different training programmes
- Can be used regardless of weather
- Available at any time
- Little space required
Drawbacks
- High purchase costs
- Unbalanced training, as the same muscle groups are always trained
The types – sitting, lying or rowing
There are many different types of ergometers. Interested persons should first consider whether a classic bicycle ergometer or perhaps a recumbent ergometer, a spinning bike or a rowing ergometer is more suitable for them. It is also important to clarify in advance how an ergometer differs from an exercise bike.
The difference between an ergometer and an exercise bike
The terms ergometer and exercise bike are often used as synonyms, but there are some differences between the two – especially in the technology. Unlike an exercise bike, which runs on batteries, an ergometer has a power connection. For example, an ergometer produces more power (from 250 watts) than an exercise bike, which usually produces no more than 140 watts. Accordingly, the resistance power of an ergometer can be adjusted to the exact wattage and thus with great precision, whereas this is not the case with an exercise bike, which usually has to be adjusted manually. Unlike ergometers, exercise bikes also do not allow power measurement, which considerably limits their range of application. If you want to improve your fitness in a very targeted way, you are better off with an ergometer. Legislation also draws a clear dividing line: while an ergometer must meet the European standard EN 957-1, this is not required for an exercise bike.
The right model for everyone
On a classic ergometer, users almost feel like they are on a bicycle: they sit on a saddle, grip the handlebars and pedal. That is why the bicycle ergometer is especially recommended for cycling enthusiasts. However, there are other types of ergometers that are suitable for different user groups:
The recumbent ergometer: The first choice for back problems
The recumbent ergometer has the user in a semi-recumbent position, which supports the back. Instead of a saddle, it has a bucket seat. The holders for the hands are located to the left and right of the seat. Thanks to the gentle motion sequence, the back and lumbar region are less strained, while the hips are mobilised.
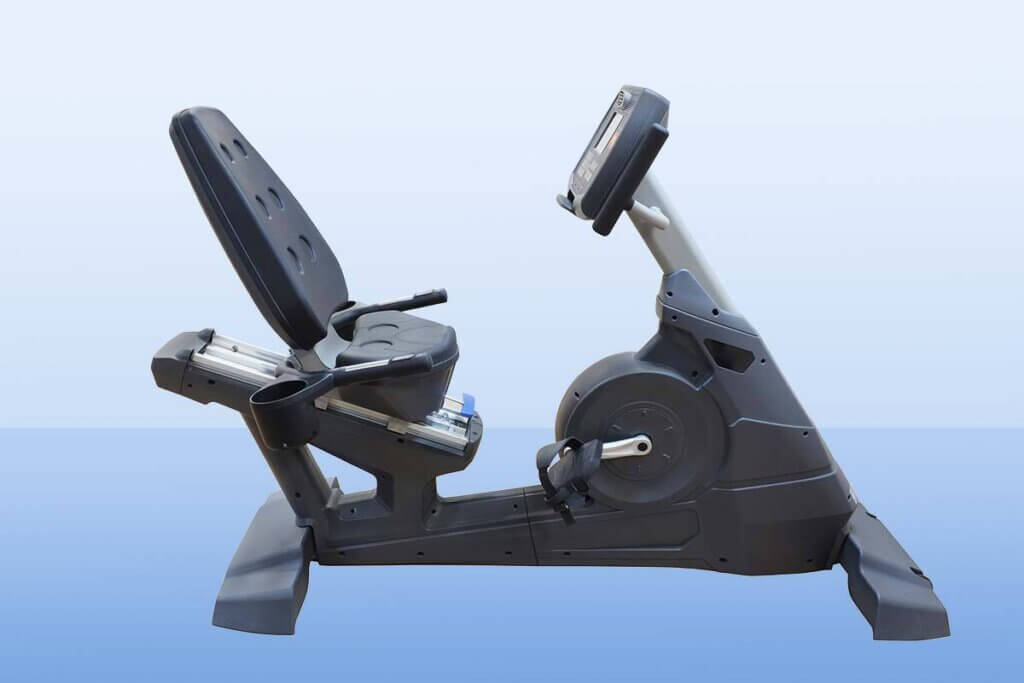

The reclined seat and backrest make recumbent ergometers suitable for anyone with spinal or lower back problems. This safe, comfortable position is the best choice for seniors who want to stay fit as they age. Thanks to the relief it provides to the spine, the Recumbent Bike is mainly used in the rehabilitation sector. However, the recumbent bike is not only suitable for people with back or weight problems, but for anyone who prefers a comfortable lying position. However, the workout should not be underestimated, because the leg and buttock muscles are even more strained here than on an ordinary ergometer.
The spinning bike: professional models for demanding cyclists
The so-called spinning bike, also known as a racer bike or indoor cycling bike, is modelled on a racing bike and is mainly known from fitness studios. In the meantime, however, it is also used in the private sector. Due to the particularly large (65 centimetre diameter) and heavy flywheel mass (18 to 25 kilograms), which has a greater moment of inertia, training requires a considerable amount of energy.
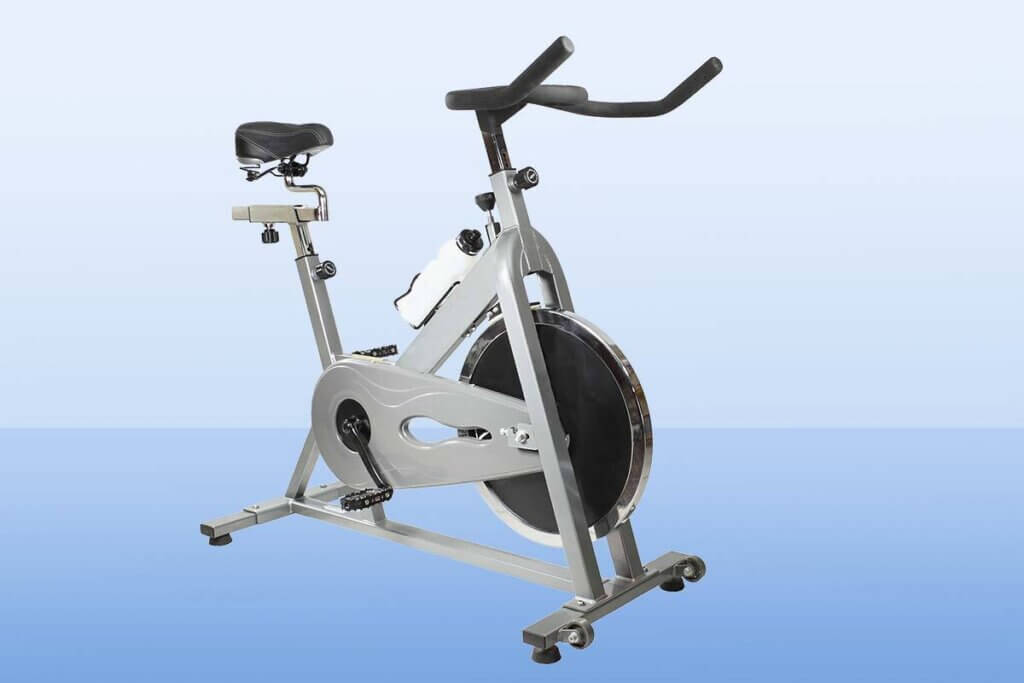

Compared to a classic ergometer, the spinning bike is designed to apply a lot of force to the pedals in a sporty sitting position. This creates a very realistic feeling of riding with high accelerations. Freewheeling (the user no longer pedals so that the pedals stop) is not possible here, however. This means that the pedals move as long as the flywheel mass rotates. For extra safety, spinning bikes are equipped with an emergency brake.
Especially ambitious cyclists and fitness enthusiasts who want intensive fat burner and interval training units get their money’s worth with spinning bikes. In addition, the high-performance bikes are also suitable as effective training devices for the cardiovascular system.
The rowing ergometer: Water sports in the dry
With the help of a rowing ergometer, exercisers simulate the movements of a rowing boat, also called indoor rowing, in order to measure and optimise their physical performance. A basic distinction is made between magnetic, wind and water propulsion, with the latter best reflecting the movements of rowing in a boat. The feet are positioned on the foot boards. An effective workout requires not only an ideal sitting position, but also a good distribution of strength between arms and legs. Powerful, but at the same time smooth and even movements are important.
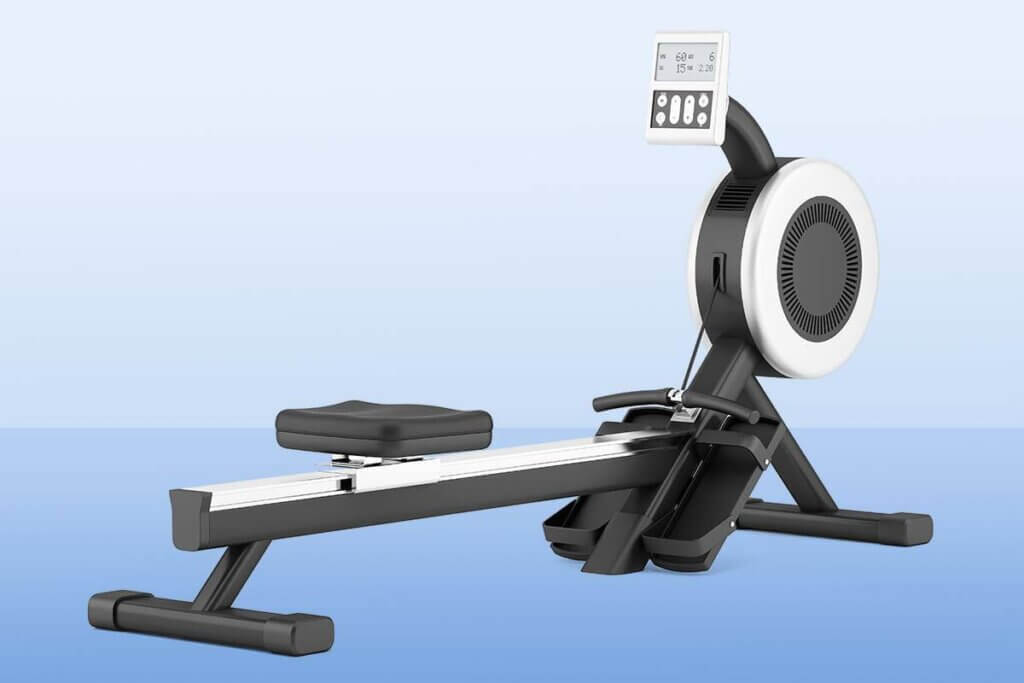

The fitness machine is also suitable for fitness training, activating the cardiovascular system and strengthening the shoulder, arm and back muscles in a uniform manner that is easy on the joints. Rowing ergometers are also often used in cross-fit and functional training courses for a full-body workout. Another plus: training with a rowing ergometer optimises posture because it strengthens the supporting muscles of the spine.
The foldable ergometer: Ideal when space is at a premium
If you don’t have enough space in your home, you can use a foldable ergometer, also known as an X-bike because of its design. Foldable ergometers are usually only half as heavy as conventional ergometers; they weigh between 14 and 18 kilograms. Although they do not have a freewheel, this deficit is not noticeable due to their lighter flywheel mass. They can be folded up easily via a hinge in the middle and stored in a free room niche to save space. For example, they can be stowed away in a storage room. This way they are always at hand without getting in the way.
The disadvantage: specific training is not possible, because ergometers with folding function do not have integrated programmes. So if you want to do intensive cycling or strength training, a folding model is not a good choice. These machines are also not the best choice for people with limited mobility, as the folding mechanism in the middle of the frame makes the entrance high and the saddle height can only be adjusted to a limited extent. Very tall, heavy people should make sure in the product description that the ergometer is approved for their user weight. Many folding models can only support a maximum weight of between 100 and 110 kilograms.
The walking ergometer: Arm training instead of leg training
These particularly small models are mainly used for therapeutic purposes, for example for patients, senior citizens or people with disabilities, to build up arm and shoulder muscles. In contrast to conventional ergometers, the focus here is not on endurance training, but instead on pedalling with the arms.
Design and function
In the true sense of the word, an “ergometer” is a measuring device for physical performance (“ergo” comes from the Greek and means “work”). In the trade, however, an ergometer is mainly known as an endurance device for home training that measures the athlete’s performance. The indoor bike’s movement sequence is similar to cycling: Users move their legs on a pedal device while seated and hold two handles that are the equivalent of the handlebar grips on a bicycle. In terms of its construction, the fitness bike is also reminiscent of a bicycle – with the crucial difference that it is stationary, i.e. it does not move from the spot. Instead of bicycle tyres, they have feet. If you train sitting upright, you can hold on to the front handles with your hands. It is also possible to lean forward, as on a racing bike, so that the forearms rest on the armrests. In addition to a braking system, they have an on-board computer that records all the measurement data. The so-called ergometry is carried out by sensors that measure, for example, the pedal speed or the pulse. The computer uses this data to calculate training values such as average heart rate or energy expenditure.
The flywheel mass: crucial for a smooth run
The heart of an ergometer is the so-called flywheel. The flywheel is connected to the bottom bracket and pedals by a V-belt, which together form the drive system of an indoor bike.
The function of the flywheel is to ensure a smooth motion; this results in concentricity or smooth running. Basically, the higher the flywheel mass, the smoother and more natural the movements. This means that the weight and the size of the flywheel are relevant for the riding experience. If the flywheel mass is too small, the rather irregular movement makes pedalling more difficult. Although a flywheel weight of five kilograms is sufficient in principle, a minimum of eight kilograms is recommended. Large flywheels (between 50 and 60 centimetres) even have a weight of between 15 and 30 kilograms.
The braking system: for uphill and downhill rides
The flywheel is equipped with a brake mechanism that not only ensures smooth running but is also flexibly adjustable. However, the word “brake” is somewhat misleading: the brake is used to set the resistance that corresponds to the different load levels before the workout begins. It can be adjusted either manually or electrically and influences the intensity of the training. The rule here is: the higher the resistance, the more force users have to apply to pedalling.
Want some resistance? The power in watts
A high-quality mechanism allows at least 16 resistance levels (up to 30 levels on particularly high-quality models) as well as adjustment in increments of no more than 20 watts (more watts means higher resistance), ideally in increments of five or ten watts. A high number of adjustment options is essential for flexible, individually designed training. While professional athletes are well advised to use a device with at least 400 watts, an ergometer with 250 watts is usually quite sufficient for hobby athletes. The correct wattage setting depends on your personal fitness level. For example, a power of 20 to 40 watts is recommended for the beginning; after the warm-up phase, another 25 watts are conceivable. Those who want to work up a sweat should increase to 80 or even 100 watts.
An on-board computer can even be used to simulate uphill runs. These terrain simulations add variety to endurance training and are thus an additional training incentive. By connecting to a smartphone, users can use a downloaded video or a self-recorded route for this purpose.
Speed-dependent vs. speed-independent models
Ergometers are divided into speed-dependent and speed-independent models. A speed-dependent ergometer displays the power in watts, but this cannot be fixed, which means that riders must constantly check whether they are within their desired load range. With a speed-independent ergometer, riders set a specific power output in watts that they want to achieve regardless of the pedalling speed. The power in watts therefore remains the same no matter how fast and hard they pedal. If users pedal slower, the resistance increases and they have to use more force to reach the set power. If, on the other hand, they pedal faster, the resistance decreases and they achieve a more even load. Ideally, the model of choice should be a speed-independent fitness bike to enable targeted training.
Magnetic or induction brakes?
Magnetic brakes or induction brakes (eddy current brakes) are most commonly used:

Induction brakes
With induction brakes, eddy currents are generated that create magnetic fields with the help of electricity and thus brake the flywheel mass. Instead of a permanent magnet, they use an electric coil. This mechanism allows a particularly fine, infinitely variable adjustment of the power.

Magnetic brakes
Most ergometers use a permanent magnet to brake the flywheel mass. By adjusting the magnetic components, i.e. applying and removing them, the speed can be slowed down more or less. The closer the magnet is to the flywheel, the more the flywheel is slowed down. Since the magnet and the flywheel do not touch each other, both mechanisms work wear-free and quietly. Cheap devices with brake shoes or belt brakes, on the other hand, are not recommended because they do not guarantee smooth running.
The on-board computer: the cockpit for the exerciser
Ergometers have sensors and an on-board computer to measure, store and display data. The settings can be made on the display, which should be large enough for the user to easily read all the data. In addition to the date and time, you can usually read the resistance, speed, distance covered, training time and pulse rate. Some models also show the number of calories burned; however, these are only estimated values.
The sensors: grip sensors, chest straps or ear clips
The ergometer can determine the maximum heart rate, the energy expended and the average speed reached. The data obtained makes it possible to check one’s own health and performance level as well as one’s ability to cope with stress. In addition, an indoor bike can determine values for increasing training. This enables professional athletes to find out, for example, how many kilometres they still have to cover in order to consume the same amount of energy as with a conventional bicycle. Beginners, returners and semi-professional athletes also know how they can improve their condition by calling up the performance diagrams over a longer period of time.
The body values are measured with the help of sensors in the grips (hand pulse sensors on the handlebars), in a chest strap or in an ear clip. During training, the sensors measure the pulse and transmit it to the computer so that the current values can be read on the display. A chest strap allows the most accurate readings, which is why it is always preferable to the other two methods for professional monitoring, but not necessary for amateur use. The telemetric transmitter belt usually sits directly on the heart and sends the data wirelessly to the fitness bike. However, these belts are only included in the scope of delivery of professional equipment. Today, the standard is rather pulse measurement via sensors built into the handles, which transmit the heart rate to the on-board computer during the workout. To do this, however, users have to place their hands permanently on the handgrips, which severely restricts their freedom of movement. Ear clips, which are attached to the ear lobe, have the disadvantage of slipping easily.
The training programmes: More is not necessarily better
Many devices offer more than 15 pre-installed programmes as well as the possibility to design programmes themselves. However, since some consumers are overwhelmed with this offer and only use a fraction of the training programmes, a large number of programmes is not necessarily a selling point. Machines with more than 50 different programmes are at best suitable for intensive users who value a very varied workout.

However, a selection of interval and power control programmes as well as user-defined and predefined programmes are always recommended. In any case, it is important that the programmes are easy to set, even with sweaty fingers. For easy operation, the symbols should also be as self-explanatory as possible.
Modern devices allow the data of up to four people to be stored and framework data such as the personal load limit to be entered. This is particularly advantageous if several people want to take turns exercising on the device. Training becomes more effective when tailored to individual needs.
From the footprint to the accessories – what matters when buying a bike ergometer
Bicycle ergometers are available in a wide range of equipment and price categories. In the following, we will show you the most important aspects to consider when buying a bike ergometer.
For a safe stand: footprint, weight and maximum load capacity
To ensure that the unit can be easily integrated into the room intended for it, the exact dimensions must be ascertained in advance. Most units require a floor space of about one to two square metres. With an average weight of 40 to 60 kilograms, it is also important that the indoor bike is stable. The device should therefore be able to withstand vigorous body movements without tipping over. As a rule, the heavier the weight, the more stable the device. In order for the user to be able to transport the ergometer comfortably from one location to another, it usually has transport wheels.
Not every fitness bike is suitable for every body weight. However, indoor bikes can usually carry a weight of 100 to 150 kilograms. Exceeding the maximum weight can affect the stability of the ergometer.
Adjustment options for optimal seating comfort
Since a device only offers the desired success if it can be adjusted to the individual body size, the possibility of adjusting the height of the handlebars and saddle is important. This allows several people to use one machine. The correct adjustment ensures that the load on the body or joints is not too high. This can cause damage to your posture. An upright posture, i.e. avoiding a hollow back, is only possible if the handlebars and saddle are the right height and the distance to the pedals is correct. In addition, the handlebars and saddle should be vertically adjustable so that the distance can be optimally adjusted. For even better riding comfort, the handlebars and saddle can also be adjusted in their angle of inclination. While some ergometers can be adjusted with a lever or knob, others have a scale or numbering. The rule here is: the finer the adjustment, the better.
The shape of the handlebars should also offer different grip positions that allow the forearms to rest in a relaxed position. Often the distance to the stem is too small, which restricts freedom of movement. The step-in should also be deep enough (especially in the case of knee problems) to allow comfortable mounting.
Handling and comfort: Ergonomic designs prevent poor posture
Comfort includes, among other things, a pleasant sitting feeling, soft, ergonomically shaped handles and a firm stand. Finally, an ergonomic design prevents bad posture. In addition, the pedals should be non-slip and comfortable. They should also have a grip loop for a secure hold. To make training as comfortable as possible, the saddle and handles should be padded with foam. The surface of the grips should be made of non-slip material so that even sweaty hands do not slip off. A saddle filled with gel is particularly comfortable because it adapts to the respective body. It is important that the saddle neither cuts into the body nor presses uncomfortably. The pedalling unit of the ergometer should also be as quiet as possible.
Seal: Tested safety
Another important point is the safety of the ergometer. Seals such as the CE or TÜV mark guarantee that the device complies with binding safety standards. The European standard EN 957-1 also classifies fitness equipment in terms of accident prevention and environmental compatibility. This includes, for example, the casing of all moving parts, which should ensure that nothing gets jammed or caught during the workout. With a good covering of all moving parts, the inside of the equipment is protected from external influences such as sweat, dirt or dust. Only with tested equipment is there a guarantee that the equipment will not show the first signs of mechanical fatigue after only a short period of use.
The devices are divided into classes A, B, C and D:
- Class A ergometers are suitable for medical and sports science purposes. Accordingly, maintenance is required frequently.
- Class B includes high-quality ergometers with freewheel function.
- Class C, on the other hand, is for simpler ergometers that do not have a freewheel.
- Machines classified as D have feet on which a normal bicycle can be installed.
Accessories and other features
There are a number of practical accessories available for ergometers that make exercising more comfortable, including
- Underlay mat: An underlay mat not only ensures a secure stand and prevents scratches in the floor, but also dampens sound, which is particularly beneficial to neighbours.
- Tablet and mobile phone holder: If you always have your smartphone or tablet at hand, you can use a fitness-related app, listen to music or watch a film during your workout.
- Bottle holder: A mounting option for the drinking bottle allows exercisers to drink while cycling.
- Saddle covers: A protective cover helps to prevent the saddle from becoming dusty or even damaged in the event of prolonged storage.
- Care products: Special care products, such as cleaning sprays, anti-static sprays and silicone sprays, keep the plastic parts clean and the grips hygienic.
- Connectivity: Some devices offer the possibility of connecting them via Bluetooth with smartphones and PCs, but also MP3 players, sound systems and televisions, for example to transmit performance data. This also makes it possible to plan routes via Google Maps, for example.
Tips for a successful workout – How to cycle properly
Once the right ergometer has been found, many people want to get on the bike immediately with motivation. However, a few adjustments need to be made beforehand. After all, the wrong sitting position can lead to pain or even joint damage. The most important and therefore first adjustment is the saddle height. The saddle should be at about hip height. To check whether this setting is correct, users sit on the saddle, put one foot on the pedal and move it to the lowest position. Depending on preference, users can also set a small angle of inclination in the saddle. However, an angle that is too high would cause pain in the abdomen in the long run, while an angle that is too low would put too much strain on the arms. The handlebar setting should also be chosen according to preference: While some prefer to cycle sportily, others prefer to sit upright – the main thing is that the back remains straight or at least only forms a slight hollow back.
The following tips will help you train effectively:
- Make sure there is variety! Although many consumers start their training enthusiastically, they lose motivation over time.
- Plan fixed times for training and stick to them. The most important thing is regularity.
- Go for longer training sessions and less intensity, i.e. resistance, if you want to boost fat burning.
- Reward yourself with your favourite music, a film or a series during your workout.
- Always keep your shoulders and hands relaxed and your head straight.
- Avoid the so-called “bent hand”! The forearm and wrist should form a line.
- Do not overexert yourself! If you experience dizziness or nausea during exercise, it is better to stop.
- As soon as you notice that your body needs a break, you should give it one. Overuse can quickly lead to joint damage, torn ligaments, torn muscle fibres or poor posture.
Appropriate training times for beginners and advanced exercisers
Basically, it is advisable to increase your performance and vary the load levels depending on how you feel at the time. Increasing the intensity is worthwhile: as soon as the body gets used to an effort, it no longer feels the need to build up muscles. It is also important to have a warm-up and a cool-down phase so that the muscles can warm up sufficiently or cool down slowly and the cardiovascular system remains stable.
The correct training duration and intervals between training sessions depend on your fitness level and training goal. For an effective workout, 20 minutes is the minimum, 35 to 45 minutes is recommended. Since beginners and those returning to exercise often do not manage this amount of time, they should first find their own pace. Although they are particularly motivated at the beginning, they quickly overtax their bodies. It is advisable to start slowly. In the first week of training, two sessions of 15 to 25 minutes each are recommended. In weeks two to four, users increase the training duration by five minutes per week. After a steady adjustment, they can do 40 to 45 minutes in the fifth or sixth week. In addition to the duration, beginners can also gradually increase the frequency of training and the number of watts. However, there should be at least one day for regeneration between the units.
If the training is advanced, the power output must be adjusted accordingly. To prevent the body from getting used to repetitive training, a varied workout consisting of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and an endurance session is a good idea. High-intensity interval training is particularly suitable if you want to burn fat. The units are comparatively short with this high load. For about 30 to 60 seconds, exercisers go to their limit of exertion before they then go for three times that amount of time at a moderate speed. This is followed by another HIIT phase. For advanced exercisers, for example, four units per week with two HIIT units and two endurance units each are suitable.
Calorie consumption
Depending on age, gender and body weight, exercisers burn different amounts of calories on an ergometer. The heavier and younger the exerciser, the higher the calorie consumption. Men burn more calories on average than women with the same physical condition. In addition, the higher the wattage, the higher the calorie consumption.
Exercise in tune with your pulse
The pulse also plays a major role in the effectiveness of training on an ergometer – it is not for nothing that all machines have a pulse measurement facility. Everyone has a maximum heart rate, which varies according to age, gender, weight and fitness level. The maximum heart rate is the number of beats that a person can achieve with the greatest possible effort. In order to estimate the intensity at which users can train, it is important to know what the maximum permissible heart rate is for which age. According to a rule of thumb, this can be calculated as follows: 220 minus the age. For a 40-year-old person, the maximum pulse rate and thus the exercise limit is 180 beats per minute. Ideally, consumers exercise at 60 to 70 percent of their maximum pulse rate.
What should not be missing is a pulse-controlled training programme. Here, the resistance is automatically adjusted to the continuously measured pulse so that users always remain in their optimal training range. The user determines in advance the maximum pulse rate that can be reached.
Abdomen, legs, buttocks: these muscle groups are worked
In the long run, ergometer training strengthens not only the leg muscles, or more precisely the front and back thigh muscles as well as the shin and calf muscles, but also the back, buttocks and abdominal muscles – without putting too much strain on the joints, ligaments and tendons. These muscles are responsible for walking upright and running. This means that training on the ergometer serves as preparation for a marathon, among other things. The bonus: The strengthened gluteal muscles give exercisers a firm buttocks.
However, users should not focus their training solely on the ergometer. Exercises with light weights for the upper body, i.e. chest, back, arms and shoulders, should not be missing from the weekly schedule to counteract imbalance.
Ergometers in the medical field
Ergometers are not only used in the private sector, but also in the medical sector, for example in physiotherapeutic practices. Since an ergometer ensures that the load remains constant, it is also suitable for people with knee or joint injuries as well as for all those who suffer from heart disease or have already had a heart operation. Athletes can use it to slowly start training again after an injury, for example.
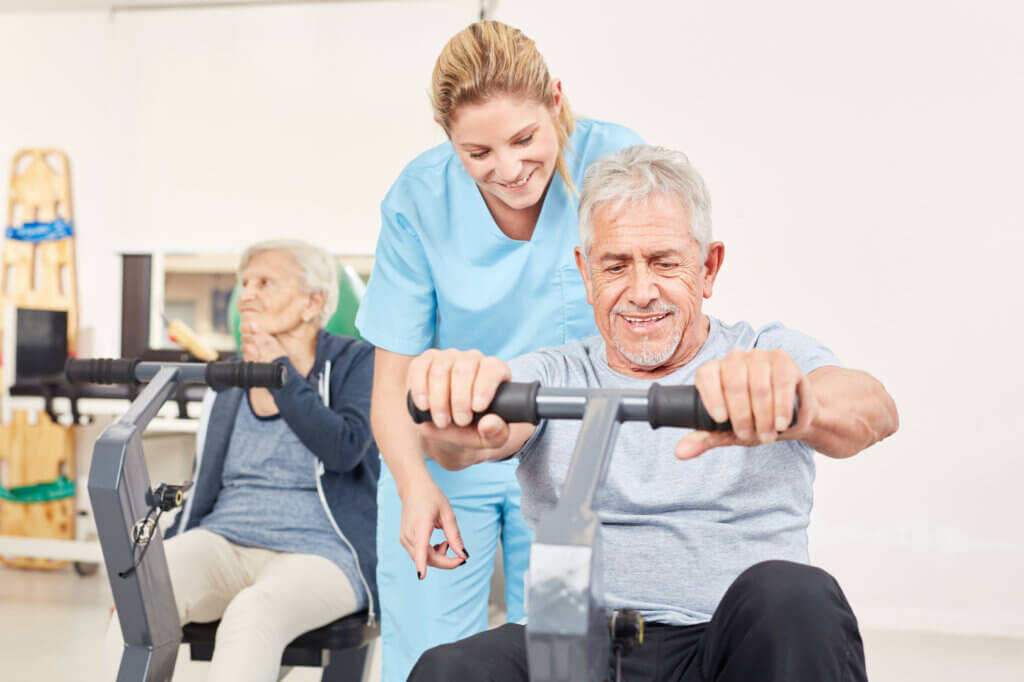

For people with knee problems, there are also special rehab pedals that can be adjusted so that the bending and extension angle can be individually adjusted to protect the knee. Patients with neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s or multiple sclerosis, for example, use an ergometer as a movement therapy device.
In addition, the devices are used in medicine for diagnostics, or more precisely as stress ECGs, to test the performance or the state of health of the heart. Doctors use them to determine whether a patient is physically fit or has a cardiovascular disease.
The best-known manufacturers – who is winning the race?
Kettler ergometers are the most common brand found in fitness studios. Since Kettler machines look stylish, they are also very popular in the private sector. Christopeit machines also perform comparatively well. The Christopeit brand is particularly impressive due to its good price-performance ratio, because despite their rather low price, the machines are characterised by stability, good ergonomics and high flywheel mass. The supplier Skandika also stands for good quality. The high-quality ergometers from Finnlo belong to the medium to high price segment. Fitness bikes from Ultrasport are particularly suitable for those looking to save money. The Horizon brand convinces not only with a modern design, but also with a high level of comfort. The Horizon range includes machines with a particularly light flywheel mass and ergonomically shaped saddles. After all, the products of the manufacturer Sportstech are mainly designed for home use.











 38,278 reviews
38,278 reviews