4K Blu-Ray player purchasing advice: how to choose the right product
- What You Need to Know
- 4K Blu-Ray players enable ultra-sharp and high-contrast playback of movies.
- To get the most out of the player, you need a 4K TV that can optimally process the transmitted picture information and a premium high-speed HDMI cable.
- Regular Blu-Ray discs, DVDs and other formats can also be played.
- You should pay attention to the compatibility of picture, video and audio formats; many devices only play a few media formats.
- A clear and comprehensible menu facilitates operation, and the most important functions should be easy to control via remote control or app.
Films in best quality
Although video streaming services are becoming increasingly popular, they are far from replacing the home player. With a Blu-Ray player, you never have to worry about your film or series juddering or stopping in the middle because the internet connection fails. The picture quality is also independent of the performance of your internet connection. It is determined by the Blu-Ray disc and the player. You have the choice between a regular Blu-Ray player with Full HD resolution and a 4K Blu-Ray player with UHD (Ultra High Definition).
The term “4K” originates from cinema production and describes a resolution of 4,096 x 2,160 pixels, “2K” corresponds to a resolution of 2,048 x 1,080 pixels in the cinema industry. In the TV sector, a different scaling has become established. According to this, a 4K picture resolution in everyday use corresponds to 3,860 x 2,160 pixels; with the alternative designation UHD, this resolution represents a further development of the previous standard Full-HD, with which conventional Blu-Ray discs work. This video format, also called 2K, works with a resolution of 1,920 x 1,080 pixels. UHD therefore has four times as many pixels as Full HD: 8.29 million instead of 2.07 million shows a clear gain in picture quality.
8K resolution
Meanwhile, manufacturers such as Samsung, Sony and LG offer TV sets with 8K. This corresponds to a resolution of 7,680 x 4,320 pixels, which results in 33 million pixels. However, there is not yet enough content and playback devices that support this format. So the current standard is still 4K.
The features of 4K Blu-Ray players
4K Blu-Ray players score points not only with the high resolution of 3,860 x 2,160 pixels, but also with very high contrasts and the ability to display up to one billion colours. This means you can enjoy ultra-sharp films that look even more brilliant and vivid. For cineastes, a UHD set is indispensable in the home cinema. The higher resolution offers a clearly visible gain in picture quality, especially with very large TVs or a small distance from the screen, while the higher contrast range and greater colour depth make a noticeable difference regardless.
HDR: You can’t do without it
4K Blu-ray players rely on HDR (“High Dynamic Range”) for more displayable colours and high contrasts. HDR renders images on TV much more realistically due to its combination of colour spectrum, brightness and contrast. The gigantic colour palette is graded in detail so that HDR even reproduces black and white intensively. With HDR sets, even scenes in the shade can be seen when the sun is low in the sky, without the sky appearing over-illuminated. In contrast to SDR (“Standard Dynamic Range”), TVs with HDR use three to five times the maximum brightness for this contrast.
With HDR, a distinction can be made between static and dynamic HDR. Static HDR is the contrast that a TV set can achieve within a picture. Dynamic contrast describes the difference between the darkest value in one picture and the brightest in another, so that the brightness of each scene can be adjusted.
There is no established standard for dynamic HDR enhancement; instead, Dolby Vision and HDR10+ compete with each other. HDR10+ was developed by Samsung and Amazon Video and is supported by many other companies. These include:
- 20th Century Fox
- Panasonic, and since 2019.
- Philips and
- Sony.
UHD Blu-ray players with dynamic HDR use either one of the two, sometimes both. The Dolby Vision process invented by Dolby Laboratories can be found, for example, at:
- LG
- Sony
- Philips
- Panasonic and
- TLC.
What else is important
To get the most out of your 4K Blu-Ray player, the player and TV must support the same format. In principle, you can also use the UHD player with a low-resolution TV; however, in this case the full 4K resolution will not be displayed. The UHD Alliance designed the logo “Ultra HD Premium” to identify the TV sets that can display HDR in full. The HDR standard of the TV must also match that of the 4K Blu-Ray player.

The connection is also an important purchase criterion. For 4K Blu-Ray players, an HDMI cable with a refresh rate of 60 hertz and a bandwidth of 18 gigabytes per second is recommended. You can recognise it by the premium high-speed HDMI label on the packaging. While a high-speed HDMI cable without a premium label is also UHD-compatible, the refresh rate of 30 hertz at a bandwidth of about ten gigabytes per second is significantly lower, so less picture information is transmitted to the TV. With a premium high-speed HDMI cable, you enjoy all the benefits of 4K films, for example the expanded colour space, with a high-speed HDMI cable you have to reckon with losses in signal transport.
Is a 4K Blu-ray player worth it for me?
If you already have a 4K TV in your living room, a suitable player is the ideal complement. Since a 4K Blu-Ray player is backwards compatible, you can also play normal Blu-Ray discs or old DVDs without any problems. You therefore do not need several devices at the same time. UHD players are a good way to exploit the full potential of the 4K TV. Although the selection of UHD Blue-Ray discs is still manageable compared to regular Blue-Ray discs, as the number is steadily increasing, a 4K Blu-Ray player is an investment for the future.
If you don’t own a 4K TV and don’t plan to buy one in the near future, a 4K Blu-Ray player is not necessarily worthwhile. If you buy a UHD player in conjunction with a new 4K TV, you can again match both devices.
Pro Points
- Picture resolution of 3,860 x 2,160 pixels
- HDR: High contrasts and better colour representation
- Downward compatible: Also plays Blu-rays and DVDs
Drawbacks
- 4K TV required for optimal results
- The improvement is hardly noticeable at a greater sitting distance
- More expensive than regular Blu-Ray players
What to look for when buying
We have already described that you need a TV with 4K resolution to enjoy the benefits of a 4K Blu-Ray player. Now, if you want to be able to see every little bit of your favourite movies while watching them with a 4K player, you should first take stock. What are the features of your TV and what connections does it have? If you are using an AV receiver in a home cinema setup, it is important that it is UHD and HDR ready, otherwise there will be a loss of picture quality. If the receiver is not compatible, they will have to connect the 4K Blu-Ray player and the TV directly. However, this will output the sound through the TV’s internal speakers instead of the speakers connected to the AV receivers.

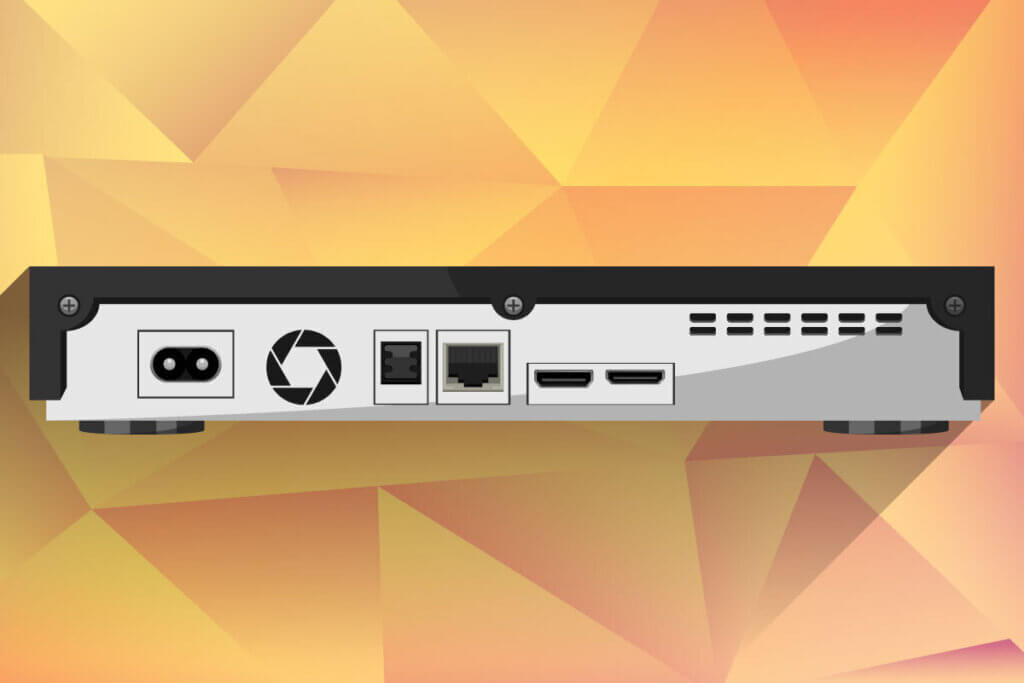
Connections for every need
You connect 4K Blu-Ray players to the TV or to the UHD-compatible AV receiver with a high-speed HDMI cable, ideally with a premium label. If the receiver is not compatible, make sure you have a second HDMI connection. This way, the player can be connected to the TV and the receiver, which then only receives the sound from the disc. Some home cinema systems do not have an HDMI connection; in this case, look for a digital sound output on the player so that you can still use the 4K Blu-Ray player with the home cinema system. However, this sound output limits the sound quality. Immersive sound is only possible by connecting via HDMI.
An internet connection can also be set up with a 4K Blu-Ray player; with most devices, this is only possible with a LAN connection. Some devices are also equipped with WLAN, but they are in higher price ranges.
A USB port is very practical if you want to output various images, videos or audio from external hard drives or USB sticks on the TV.

Compatible playback media
In general, 4K Blu-Ray players are backwards compatible. This means that regular Blu-Ray discs, DVDs and audio CDs can be played without any problems. However, playing 3D Blu-Rays is not necessarily possible. So if you have a large number of 3D Blu-rays in your collection or would like to buy 3D films in the future, you need a UHD player that also plays them. Such a device is usually no more expensive than a UHD Blu-Ray player without this function.
If you want to use the USB port for playing pictures, videos and audio files, you should make sure that the device can play a large number of formats, such as MOV, MP3, MP4 or JPEG
Picture quality: 4K upscaling and HDR
In terms of picture quality, 4K Blu-Ray players often use a trick to improve the resolution of regular Blu-Rays: Upscaling. An upscaler built into the device uses interpolation technology to do this. If you put a Full HD disc into a UHD player, the upscaler calculates suitable additional pixels from the individual pixels and places them in the missing space. Thus, two million pixels result in more than eight million pixels. This noticeably improves the picture resolution, but it does not reach the picture quality of 4K films. Not every 4K Blu-Ray player with an upscaling function is able to upscale DVDs with 720 x 576 pixels to 4K. If you have a large collection of DVDs and Blu-rays, it is advisable to take a closer look at the upscaling function.
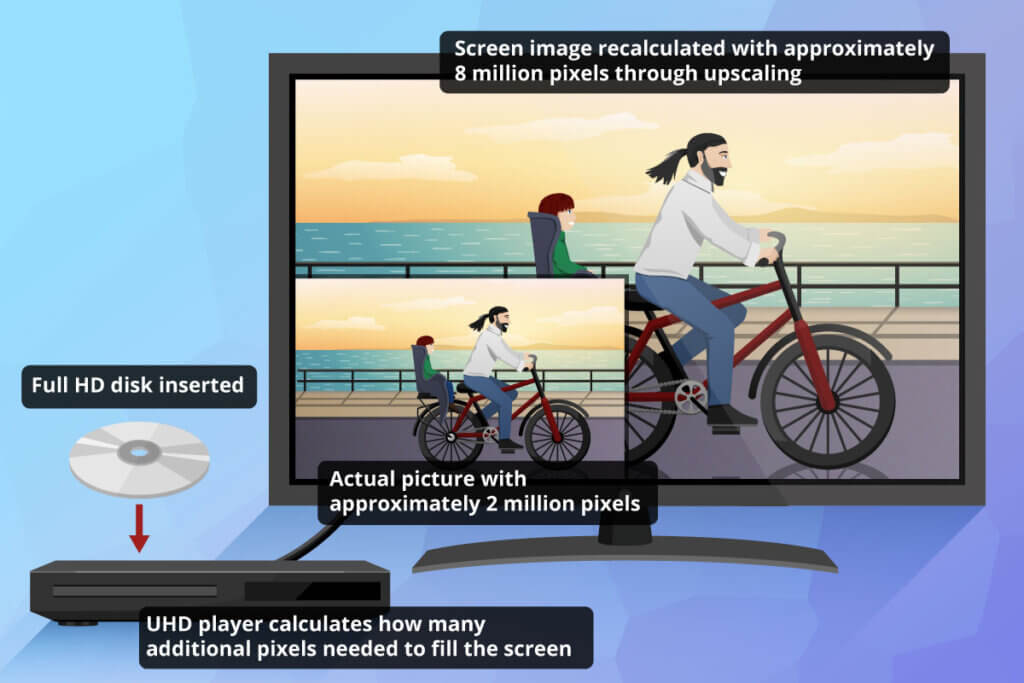
As with TVs, there is no uniformity in terms of HDR technology on 4K Blu-Ray discs: some use only one of the two dynamic processes and some discs encode the information in HDR10+ and Dolby Vision. In terms of the best possible playback of your favourite films, you are therefore limited if your devices only work with one of the two processes. Playback is possible, but in static HDR10.
If you want to enjoy every UHD disc in the best possible picture quality, we recommend a TV set and a 4K Blu-Ray player that are compatible with both dynamic HDR processes. These are, for example, newer models from Panasonic. As a rule, however, it is sufficient to go with your existing setup.
Smart or not?
Often, 4K Blu-ray players offer pre-installed apps and the option to download them. This means that streaming services such as Netflix can be easily accessed via the player. However, if you have a Smart TV or streaming sticks such as Amazon’s Fire TV Stick 4K or Google’s Chromcast, you do not need to attach great importance to possible apps. You only need apps for the Blue-Ray player if your TV set itself has no or few apps or if you do not use an external streaming solution.
More important: Operation
A clear and comprehensible menu simplifies the setting of the player and the adjustment to the desired playback media. A so-called last-scene memory function allows you to continue playing the film at the right place after interruptions. This eliminates the need to search for the scene in the chapter overview. The remote control should be designed so that you can control all important functions with just a few clicks. This includes an intuitive arrangement of the buttons as well as clear labelling. Some higher-priced models allow you to operate the 4K Blu-Ray player with the help of a smartphone app, which provides additional convenience but is not absolutely necessary.
Game consoles as an alternative?
If you own an Xbox One S or X, you can play UHD Blu-Ray discs with these consoles. However, the devices do not offer dynamic HDR. A normal consumer who owns one of the two consoles can thus save money; cineastes, on the other hand, should buy a separate 4K Blu-Ray player with more options.
Some basic terms
When searching for the right 4K Blu-Ray player, you may have come across some terms that were initially unfamiliar to you. After all, the entertainment industry is constantly changing and coming up with new technological advancements. Knowing a few basic terms will help you weigh up the various models and innovations, including in the area of UHD players.
4K/Ultra-HD
In everyday language, 4K, Ultra-HD and UHD refer to the same thing: a picture resolution standard of 3,860 x 2,160 pixels established by the television industry. This resolution thus has four times the number of pixels of the previous standard Full-HD (2K) with its 1,920 x 1,080 pixels. In cinema production, from which the designations “4K” as well as those of the previous standard “2K” originate, it is 4,096 x 2,160 pixels to 2,048 x 1,080 pixels.
ARC and eArc
ARC stands for Audio Return Channel and is a feature of the HDMI interface. It improves communication between the TV and the connected audio hardware. You don’t need a data cable to get the best sound. The eARC (Enhanced Audio Return Channel) is a further development of ARC with a larger bandwidth, so that formats such as Dolby Atmos can also be transmitted. The channel is an integral part of HDMI 2.1.

Pixels
Better known as pixels, they represent the smallest unit on the display panel. The higher the number of pixels, the more detailed, finer and sharper the picture usually is.
Refresh rate
The refresh rate indicates, in units of hertz, how often a display can change the image it shows. It is also called frame rate. A fast picture repetition is necessary so that the eye perceives the pictures as continuous movement. The higher the frequency, the smoother the display.
HFR (High Frame Rate) enables a higher frame rate per second. Whereas films were previously shown at 24 frames per second, HFR allows 48 frames per second in Full HD and up to 100 frames per second in Ultra HD. With this technology, even fast motion sequences in films can be displayed in detail and realistically.
Candela and Nit
Candela per square metre and Nit describe the luminosity of the TV set. The higher the values, the brighter the pictures.
Dolby Digital/ DTS
Dolby Digital and DTC describe two competing sound systems that are used in different versions in cinemas and on DVDs and Blu-Ray discs. For HD media, Dolby developed Dolby TrueHD, for example, while DTS created DTS-HD Master Audio. 3D sound, i.e. immersive sound, is achieved by both providers with Dolby Atmos and DTS:X. These sound formats can also be used with DVDs and Blu-ray Discs. These sound formats can also be played back with 4K-compatible devices.
SDR and HDR
SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) describes a contrast with 256 variants of the primary colours red, green and blue. A conventional TV set thus displays 16.7 million colours. HDR (High Dynamic Range) allows 1,024 gradations of each primary colour and thus over one billion colours. Static HDR reproduces the entire film with constant parameters in terms of brightness and colour representation, while dynamic HDR adjusts the parameters to each individual scene.
















 1,122 reviews
1,122 reviews






